What is Managed File Transfer (MFT)?
Managed File Transfer (MFT) is a software solution that simplifies internal and external data transfers for businesses. Thanks to MFT, transfer processes can be seamlessly automated, configured, and managed. In doing so, a high level of transparency and safety is guaranteed. Find out what the advantages and disadvantages of MFT are and where it’s used.
How does MFT work?
Managed File Transfer is available as an on-premises application or as a cloud service (SaaS). This distinguishes it from pure network protocols like File Transfer Protocol (FTP) or SSH Transfer Protocol (SFTP). First, the files are uploaded and encrypted in the MFT system. Here, secure protocols like FTPS, SFTP, or HTTPS are used as connections. These transmit the data to the target system or to other applications. All activities are logged to ensure that they meet compliance requirements. Archiving also simplifies subsequent follow-up checks.
The infographic shows how data is exchanged between internal and external systems with MFT:
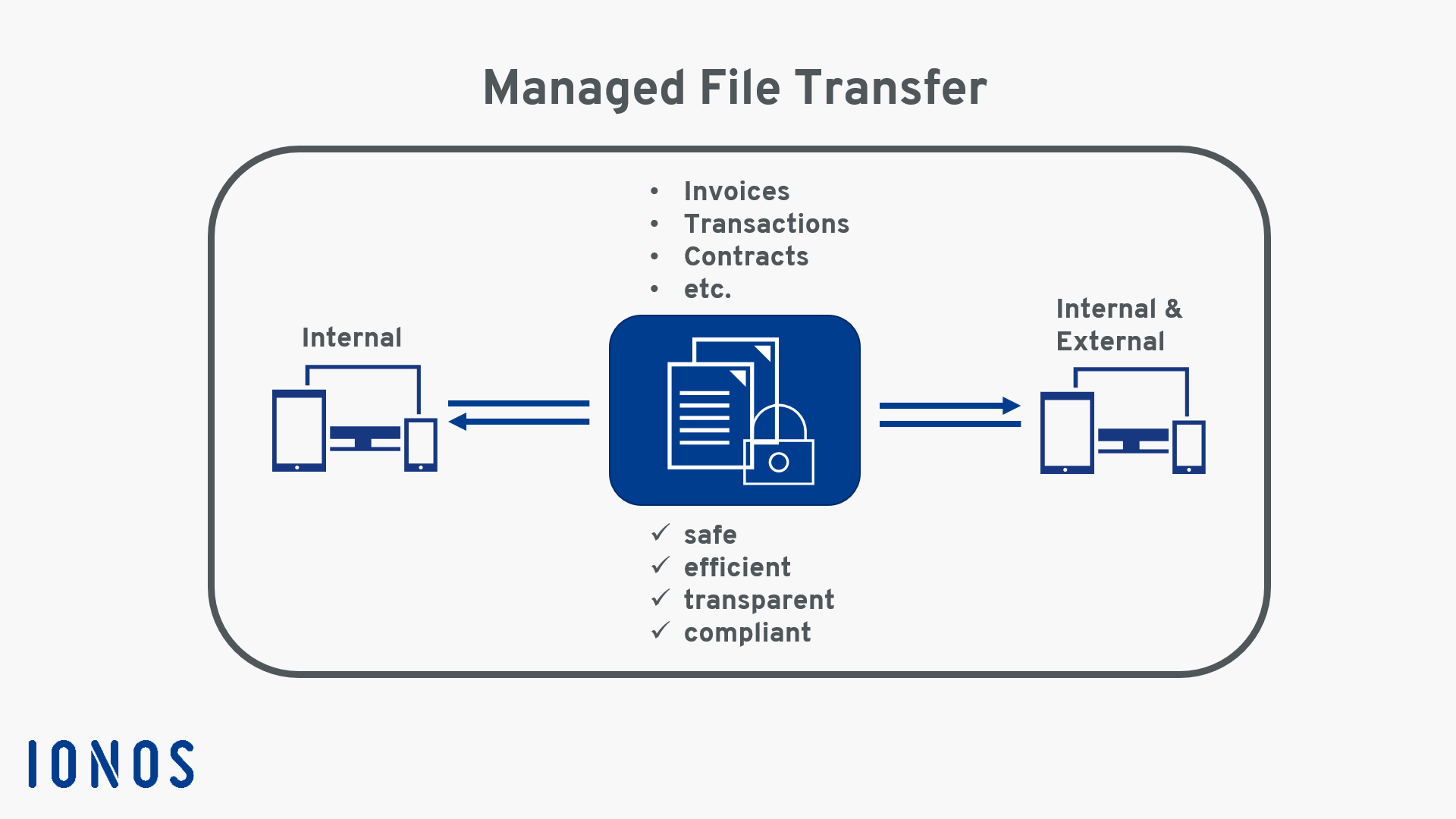
What are the advantages of MFT?
Advantage 1: Safety
MFT solutions usually include cryptographic measures like end-to-end encryption (E2EE) to protect data during transfer and when idle. This makes MFT more reliable and involves fewer risks than FTP. Regular security checks and real-time monitoring also prevent costly data breaches.
Advantage 2: Efficiency
Data is exchanged securely and efficiently between systems and locations. This includes large data volumes. In addition, Managed File Transfer supports extensions for a wide range of platforms, mobile devices, databases, and applications like ERP and CRM.
Advantage 3: Compliance
Organizations can configure MFT to meet stringent security standards. This includes regulatory requirements like the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Payment Card Industry Data Security Standards (PCI DSS), Basel II, Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Sarbanes-Oxley Act (SOX).
Advantage 4: Transparency
With the high level of transparency provided by logging processes, risks can be better assessed. Errors in data transfers can be corrected more quickly or prevented altogether.
What are the disadvantages of MFT?
Disadvantage 1: Cost
MFT is typically more expensive than setting up an FTP server, since specialized hardware and software components are required for the extensive functionalities.
Disadvantage 2: Complexity
As a software platform, MFT is more complex to implement and requires a certain technical understanding. Employees must first be trained in how the system works.
Disadvantage 3: Maintenance
Local MFT systems need regular maintenance to remain secure. This is often resource intensive and time consuming. But Managed File Transfer is also available as SaaS, where updates and maintenance are handled automatically by the provider.
Where is MFT typically used?
Managed File Transfer is particularly suited for companies that need to manage and transfer large amounts of sensitive data. MFT is frequently used in these areas:
- Financial services: MFT can be used to securely transmit sensitive financial information like account details, transactions, or credit card data.
- Healthcare: Hospitals or doctors’ offices can use MFT to manage and transmit electronic patient records, lab results, or X-rays according to security standards.
- Government agencies: Government entities benefit from Managed File Transfer when transmitting secret and classified information like tax or customs data.
- E-commerce: E-commerce often generates high volumes of data like orders, invoices, and transaction data that can be efficiently logged and exchanged between companies and customers with MFT.

