What are the different types of domains?
If you’re looking to run a website or online store, you’ll undoubtedly be faced with the challenge of finding a suitable web address. With the many different domain types out there, though, finding the right domain is often not as simple as it looks. For one, you’ll need to decide on a strong and unique name, whereby the second-level and third-level domain types play an important role. On the other hand, you’ll need a suitable domain ending, also known as a top-level domain.
Are you looking for the perfect web address name for your online project? With IONOS you can register a domain – including an SSL/TLS certificate and a personal email domain!
The following guide will clear up the most important questions on domain types. What types of domain endings exist and what do they mean? How do the different domain levels within a domain name differentiate from one another? And how can you find out which type of domain is best suited to your project?
- Free Wildcard SSL for safer data transfers
- Free private registration for more privacy
- Free 2 GB email account
What is a domain?
The Internet connects technical devices and services across the whole world. This is made possible among other things by the protocol stack TCP/IP and the domain name system (DNS). TCP/IP makes sure that every computer and every mobile device as well as every web service that is available via the Internet has a clearly defined IP address such as 93.184.216.34. The DNS translates these addresses using name servers into human-readable domains like www.example.org. This process is also called name resolution.
When you want to access websites and online stores via a browser’s address bar such as Firefox or Google Chrome, or you want to connect to a server or another device on the Internet, you end up contacting these individual domain addresses.
Overview: what types of domain name and endings are there?
A web address can cause a lot of headaches. On the one hand, this is because a good, catchy name is not that easy to find. On the other hand, it’s complicated, especially for inexperienced web project operators, to keep track of the various domain types and levels available.
Here, we’ll introduce you to the five most important components and types of domains (including examples) to know before moving ahead with a successful domain registration.
Our Digital Guide has more useful articles on how much a domain costs and how you can find out how much a domain is worth.
Top-level domain (TLD)
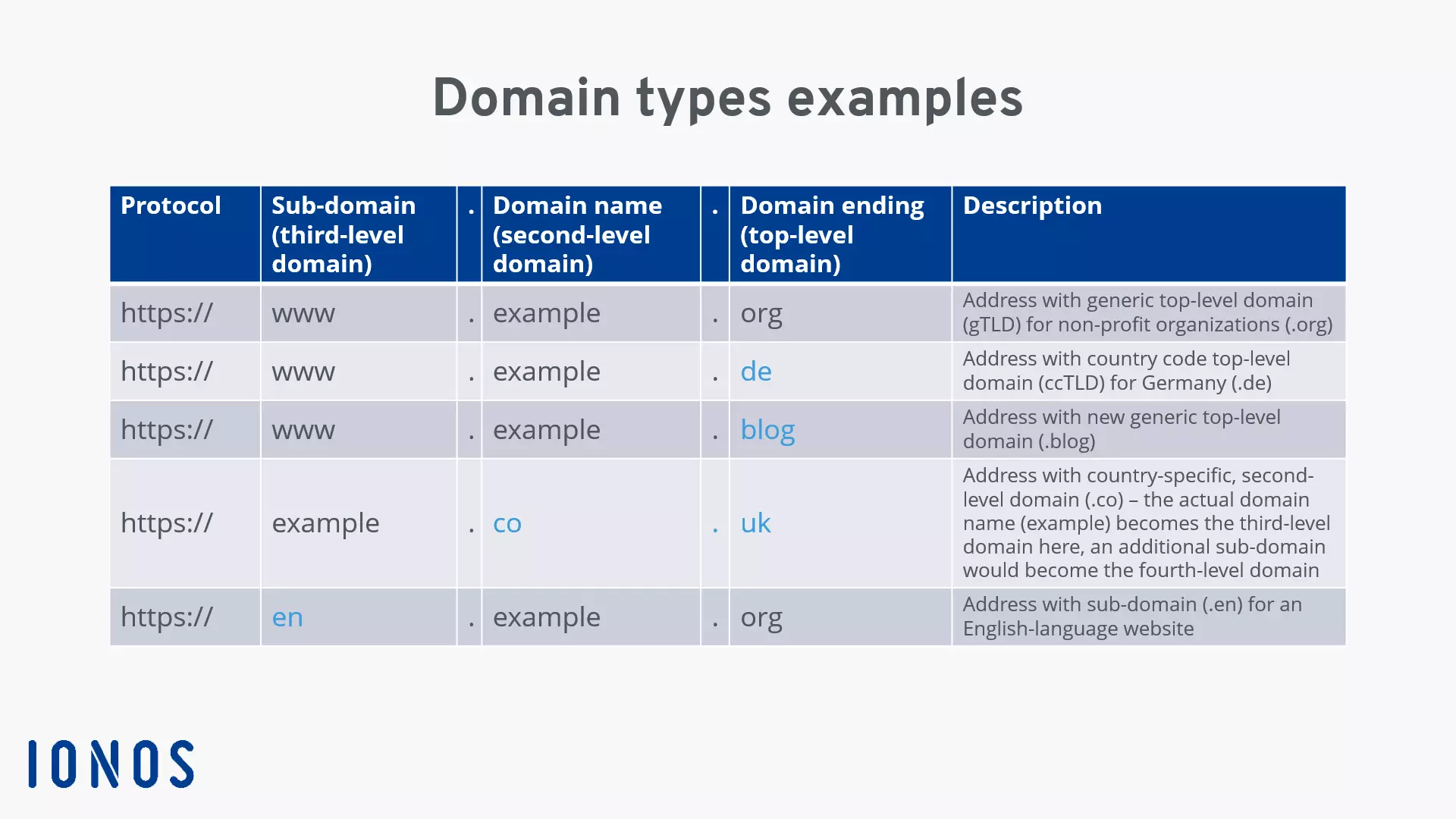
Top-level domains, or TLDs for short, represent the highest level of name resolution in the domain name system hierarchy. As a domain component of the highest level, a top-level domain always appears as the last part of a web address (to the right of the last dot), which is why TLDs are also referred to as domain endings. In the domain example already used, www.example.org, the top-level domain is the address part org.
The allocation of TLDs is managed by IANA, a division of ICANN (Internet Corporation for Assigned Names and Numbers), an organization founded in 1998. IANA determines which domain endings exist and sells the rights to assign them to registrars, who in turn negotiate with domain providers on the sale of the now more than 1,000 domain endings.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
For most existing domain extensions, there are no concrete restrictions. However, while publishing new TLDs, which have been gradually released since October 23, 2013, some registries have decided to rely on exclusivity in the allocation process. Learn more about this topic in our detailed article on exclusive top-level domains.
When web addresses were first launched, there were initially only the following seven top-level domains:
| Original top-level domain | Original meaning of the domain ending |
| .com | Open domain for commercial web offers |
| .org | Open TLD for non-profit organizations |
| .net | Open address for Internet service providers |
| .int | Strictly limited extension for internationally operating companies, organizations, and programs |
| .edu | Domain intended for trade schools and universities |
| .gov | Domain for US government institutions |
| .mil | TLD available only to departments, services, and agencies of the U.S. Department of Defense |
- Intuitive website builder with AI assistance
- Create captivating images and texts in seconds
- Domain, SSL and email included
ccTLDs (country code top-level domains)
ccTLDs are a special category of domain extensions administered by the respective country. ccTLDs always consist of two letters, e.g., the codes de for Germany or uk for the United Kingdom. In addition to country code TLDs, ICANN has also assigned ccTLDs for dependent territories that are geographically separated from the parent country. For example, parallel to the Australian domain .au, there are also ccTLDs for the Cocos Islands (cc), the Christmas Islands (cx), Norfolk Island (nf) or Heard and McDonald Islands (hm), all of which are Australian outlying territories.
The guidelines that apply to registering a country-specific domain are up to each country. Many smaller and poorer countries have taken advantage of this fact and marketed their ccTLD specifically. For example, the dwarf state of Tuvalu sold its domain to the company DotTV for 50 million dollars and invested the money in IT infrastructure. Tuvalu was also able to pay the fee for its admission as the 189th member of the United Nations on September 5, 2000, from the “.tv-deal”. More information and key facts can be found in our detailed article on the topic of ccTLDs.
The following table presents some country-specific TLD examples:
| Country-specific top-level domain | Domain ending meaning |
| .ch | Switzerland |
| .cn | China |
| .de | Germany |
| .eg | Egypt |
| .es | Spain |
| .fr | France |
| .it | Italy |
| .ru | Russia |
| .uk | The United Kingdom |
| .us | The United States |
gTLDs (generic top-level domains)
The domain type of the so-called generic top-level domains differs from country-specific addresses in that it does not cover a geographical area, but a thematic area. In addition, generic addresses are divided into two types:
Non-sponsored gTLDs are subject to centralized control and management by ICANN, which cooperates with various partners for this purpose. Originally, these endings were to be assigned only under certain conditions: For example, the domain .net was meant to be reserved exclusively for Internet service providers. Today, like many other non-sponsored gTLDs, it is also available for other companies and organizations as well as for private individuals.
Sponsored gTLDs, on the other hand, are subject to the restrictions determined by the respective sponsor. In this case, the respective independent companies or organizations are also responsible for the administration and control of the gTLDs. A sponsored domain example is .gov, which to date has been administered by the US authorities as sponsor and is used for American government websites or services.
| Examples of sponsored gTLDs | Domain ending meaning |
| .gov | US government agencies |
| .mil | US military |
| .aero | Aviation industry |
| .jobs | Job postings |
Detailed information and a full listing of all gTLDs can be found in our article “What is a generic top-level domain (gTLD)?”.
The new top-level domains released at regular intervals since 2013 like .blog, .web or .beauty count towards generic top-level domains.
Second-level domain (SLD)
A second-level domain is the freely selectable name below any top-level domain. For this reason, this component of a web address is also called the domain name. Although it is located below the TLD in the domain hierarchy, the second-level domain is by no means less relevant than the ending. The real situation tends to be the other way around: the domain name is much more important than the extension from both a user and SEO perspective, as it can better describe the content of a site and even contain keywords.
In our domain example www.example.org the second-level domain is “example.”
The assignment of an SLD always takes place with the desired superordinate top-level domain!
There are even some country-specific, second-level domains, as displayed in the below table of combination examples with the TLD .uk:
| Examples for country-specific second-level domains | Domain ending meaning |
| .co.uk | Commercial web offerings in the UK (United Kingdom) |
| .gov.uk | Central and regional government agencies and services in the UK |
| .me.uk | Private individuals in the UK |
| .sch.uk | Schools in the UK |
Third-level domain (sub-domain)
Optionally, another domain level can be subordinated to the domain name. This type of domain is placed before the second-level domain and is called a third-level domain or sub-domain. The function of such a third-level domain is to structure the contents of a website or web store in a meaningful way. Different topics or different language versions of a project can be clearly marked in the web address, while the domain name remains unchanged.
In the domain example www.example.org, the well-known sub-domain www is used. Particularly in the early days of the Internet and the world wide web, this signaled to users that they were dealing with a web application, for example a website with information. Today, however, since it’s no longer necessary to enter the third-level domain in order to visit a website, it’s becoming increasingly rare to come across operators who advertise their website including the “standard” third-level domain, www. More common sub-domains that you encounter much more often nowadays look like the following – staying with the domain example example.org:
- en.example.org
- es.example.org
- it.example.org
- de.example.org
The above shows a typical division into sub-domains for the different language versions of the “example” website. The third-level domain en is used to identify English-language content, while Spanish content can be found under the sub-domain es. The German-language part of the web project runs under the third-level domain de, and Italian users will find content in their native language when visiting the sub-domain it.
In theory, all domains below the top-level domain (TLD) are sub-domains of the preceding one, although in practice they are rarely called sub-domains. The domain name (second-level domain) is a sub-domain of the TLD, the third-level domain is a sub-domain of the second-level domain, and so on. For country-code second-level domains such as “.co” in example.co.uk, the actual domain name (“example”) becomes the third-level domain. A sub-domain of this would then be a fourth-level domain. In principle, the number of domain levels is unlimited. However, to be able to remember an Internet address well, it’s usually limited to three levels.
More basic information on third-level domains including instructions for creating a sub-domain for your own web project can be found in our guide “What is a sub-domain?”.
How to choose the right domain type or domain name?
Knowledge of the hierarchical structure of web addresses and domain extensions can be helpful when it comes to finding the perfect domain. However, you should be careful not to complicate the design of your web project’s address unnecessarily. In the end, a domain should always suit you and your project and make it as easy as possible for users as well as search engines to find your pages.
Finally, for this reason, we’ve summarized some elementary tips and tricks that will make choosing the right type of domain and extension much easier.
Tip 1: Decide on targetable domain types
Creating sub-domains doesn’t always make sense. A sub-division of your web address can also be confusing to web visitors, for example, if you generally don’t have a lot of content or if the sub-domain distracts too much from the actual domain name. Therefore, only decide to use an individual third-level domain if you have a clear concept in mind for this. A specific sub-domain is useful for the following scenarios, among others:
- Differentiation of different language versions
- Separation of content from other offers such as a service area, a blog, or a forum
- Marking a specific web service such as an app or an FTP server
- Operating an online store in parallel to the website under the same second-level domain
Tip 2: Choose a top-level domain that fits your project
When it comes to choosing the domain extension, it is not only the budget that plays a role. If the top-level domain does not match the content orientation or style of your web project, this is not necessarily negative from either a user’s or search engine’s perspective. For example, if you choose the generic top-level domain .shop, visitors and Google will assume that your project is a web store. This may lead to negative reactions if this is not the case at all and you are neither involved in e-commerce or stationary trade.
Tip 3: Ask for help
Even if you have found the right domain type from your point of view and are satisfied with the complete package including name and extension, you should not rush the registration of your web address. Ask friends and acquaintances or colleagues for a serious and honest assessment of your domain. Outsiders will have a different perspective on the appropriateness of your web address so be sure to take advantage of the opportunity to get a second opinion to always be on the safe side when choosing domain type and domain name.
Find the perfect domain name for your business with the AI Domain Name Generator from IONOS.