What is an SMTP Server?
Interestingly, the path of a sent e-mail doesn’t follow a straight line. Typically, an e-mail will not simply travel from sender to recipient, but instead completes several transitional steps along a clearly ordered process. The main players in this are the participating SMTP servers, which will ensure that the electronic mail reaches the recipient according to protocol. The internet has an entire network of such distribution stations and relays to make the movement of e-mail traffic possible in the first place.
Register great TLDs for less than $1 for the first year.
Why wait? Grab your favorite domain name today!
- Matching email
- SSL certificate
- 24/7/365 support
How does an SMTP server Work?
An “SMTP server” refers to a mail server that forwards emails from a sender to one or more recipients in accordance with network protocol regulations across the internet. One important function of the SMTP mail server is to prevent spam using authentication mechanisms that only allow authorized users to deliver emails. To enable this, most modern mail servers support the protocol extension ESMTP with SMTP-Auth.
The so-called ‘relays’ - SMTP servers are the essential link in the email transmission process - in which several servers are involved: namely the sender’s outgoing mail server, one or more external forwarding servers and the recipient’s incoming mail server.
Outgoing Mail Server of the Sender
After the sender has sent their e-mail, the webmail application or program used to send the e-mail (known as the “SMTP client” or “Mail User Agent (MUA)”) converts the message into a header and body before loading them on to the outgoing mail server – the SMTP server. The server mail transfer agent (MTA) represents the software basis for sending and receiving e-mails. The MTA checks the e-mail for size and spam and then saves it. To lessen the burden of the MTA’s role, it’s sometimes preceded by a “Mail Submission Agent” with the function of checking the email’s validity in advance. Then the MTA checks the Domain Name System (DNS) for the recipient mail server’s IP address.
External Forwarding Servers
If the recipient domain is connected to the same mail server as the sender, the e-mail will be delivered directly. If not, the MTA splits it into small data packets to be forwarded to the destination SMTP server in the shortest and least congested route possible.
Incoming Server of the Recipient
Upon arrival at the destination SMTP server, the data packets are reassembled back into a complete e-mail. This is once again checked for spam by the MSA and/or the MTA and then transferred to the message storage area in the incoming mail server. From there, the "Mail Delivery Agent" (MDA) sends it to the recipient's e-mail inbox. Then other network protocols - either IMAP or POP3 - download the electronic mail to the recipient's SMTP client.
From a purely technical point of view, it would also be possible to send e-mails directly from the sender's SMTP client to that of the recipient. However, the use of an SMTP server has a clear advantage: if the recipient’s inbox server is busy or temporarily out of service and the e-mail can’t be delivered, the SMTP server responsible will automatically try to redeliver the e-mail at regular intervals. This happens until the delivery is successful or until the e-mail goes back to the sender as undeliverable.
What SMTP server should I use?
As the sender, you have a choice of multiple SMTP servers from different providers to feed and forward your e-mails to the network. One interesting alternative that many choose is to set up your own server.
SMTP server from a provider
SMTP servers from the usual providers are generally recognized as trustworthy by other providers. Furthermore, because of the large amount of data processed, their spam filters are considered particularly strong. The main drawback of a free SMTP server is that they tend to have strict limits on the number of e-mails you can send per day, mailbox size and on the size of attachments.
Internet Service Providers: Internet service providers (ISP) such as IONOS often provide an internet connection along with the e-mail address to give access to the big name e-mail servers.
E-mail Providers: The most common way in which individuals send e-mails to friends and relatives is via a free e-mail provider’s web application, such as Gmail, Yahoo or Outlook. The only requirement is to have an e-mail address suitable for the domain with which the provider’s SMTP server can be used for personal correspondence. You just have to configure your mailbox for the correct STMP server address – you can find an overview of the most popular providers and their addresses below.
Hosting Service Providers: Many hosting packages, like those from providers like IONOS, include access to an SMTP server as standard to handle internal and external mail traffic.
Specialized Providers: Some companies specialize exclusively in leasing SMTP servers. Examples of these include Amazon SES and SparkPost where you can rent specific hardware tools at request.
- 2 GB+ storage
- Sync across all your devices
- Spam filter and ad-free

Personal SMTP server
With some basic understanding of IT, it’s also possible to set up your own SMTP server. For example, a Raspberry Pi computer teamed with the appropriate software makes an excellent hardware basis for this system.
A personal SMTP server comes with some clear advantages: no provider restrictions placed on usage, full control over all settings, and maximum data security. In addition, a self-built server is an ideal way to gain familiarity with the processes around e-mail traffic. Of course, a personal server also has its downsides: because personal internet transmits a dynamic IP address, private SMTP servers are often classified as spam distributors by major mail providers and end up in recipients’ junk folders. This issue, however, can be traversed with only a few restructuring measures and/or additional costs. On the whole, if the purpose of your SMTP mail server is just to send e-mails to other private clients, a personal server is definitely a great solution.
Overview: SMTP servers Pros and Cons
The follow table summarizes the pros and cons of servers from providers compared to self-managed server alternatives:
| Advantages | Disadvantages | |
| SMTP server from a provider | All necessary hardware provided Minimal effort required during setup/maintenance Authenticated reputation with providers Strong spam filter | Strict limits regarding e-mails, mailboxes and settings Sensitive data stored on external server Offers of a good server can be paid service |
| Personal SMTP server | Full autonomy over all settings No provider usage restrictions Maximum data security Can retrieve e-mails on any device Great for gaining insight into e-mail traffic process | Requires technical know-how Own hardware must be provided Additional costs for installation and maintenance Has a poor reputation among providers Possibly costly expenditures for restructuring Tends to have weaker incoming spam filters |
How can I find my SMTP server?
If an error occurs during an e-mail’s transmission, the problem can be rectified more easily if you know the address of the SMTP server used to send it. Since most e-mail addresses are structured in either "smtp.domain.com" or "mail.domain.com" format, they are relatively easy to remember.
The correct address for your e-mail account can be found in the account settings area of your mail program:
- In Outlook, click “Account Settings” in the File menu, select your account and click “Change”. This will open an overview of the user, server and login information.
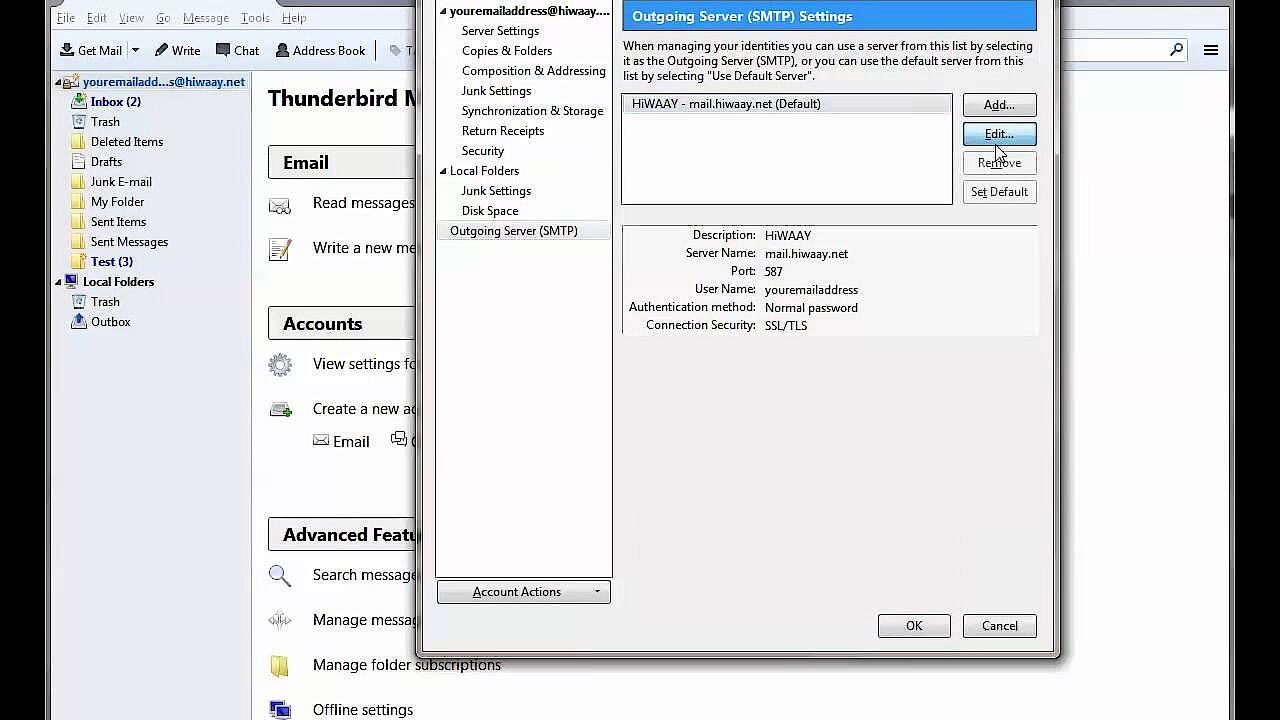
- In Mozilla Thunderbird, right-click on your account to open the pop-up menu and click on "Settings". Under the menu item "Outgoing mail server (SMTP)" select your SMTP mail server and click on "Edit".
 To display this video, third-party cookies are required. You can access and change your cookie settings here.
To display this video, third-party cookies are required. You can access and change your cookie settings here. If you’re trying to find out what your SMTP server address is for the first time - for example, during the manual configuration of your mail program – you will most likely find this in the help section of your provider’s homepage. Below is a list (current as of March 2018) of the main e-mail providers and the addresses of their free SMTP servers.
| E-mail Provider | SMTP Server Address |
| IONOS | smtp.ionos.com |
| AOL | smtp.aol.com |
| AT&T | smtp.mail.att.net |
| Gmail | smtp.gmail.com |
| GMX | smtp.gmx.com |
| iCloud | smtp.mail.me.com |
| Mail.com | smtp.mail.com |
| MSN | smtp.live.com |
| Outlook/Hotmail | smtp-mail.outlook.com |
| Yahoo! | smtp.mail.yahoo.com |
| Zoho | smtp.zoho.com |
How can I test an SMTP server?
Ensuring you have the correct SMTP server address may be necessary if your SMTP mail server isn’t functioning properly, i.e. you can’t send e-mails and have already taken measures such as checking the mail client connection settings and clearing the inbox. Once you have this, you can then clear things up using the Telnet user-command tool, which is accessible on all major operating systems.
For Microsoft operating systems in Windows Vista or later, you must first manually install and activate Telnet via the Control Panel.
Telnet allows you to manually start an SMTP session and carry out the following diagnosis:
- Check implementation of SMTP server
- Check the accessibility of all required SMTP commands
- Detect connection blockages caused by a firewall or anti-virus program
- Ensuring that a user or a particular provider domain is receiving your message
The following example demonstrates how to test the SMTP server connection from an internal client to a server using basic authentication on Windows:
1. Open the command prompt (search the term "cmd" in the search bar)
2. Enter the “telnet smtp.example.com 25” command to connect to the SMTP server via port 25 (Replace "smtp.example.com" with the address of your own SMTP server.)
3. If the server is reachable, it replies back with status codes 220 and "smtp.example.com ESMTP Postfix", or a comparable plain text message. This would indicate that the SMTP server has no connection error.
You can then authenticate and, if necessary, send a test e-mail to pinpoint the cause of the problem. If the e-mail doesn’t reach its destination after the connection has been proven as working, the issue most likely lies with your provider or the recipient.
If there’s no answer or an error message being returned from the server, your firewall or antivirus program could be one possible cause of the e-mail transmission problem. Alternatively, you can also test the SMTP server connection using an online tool such as wormly.
- Personalized email address
- Access your emails from anywhere
- Highest security standards


