CRC errors: explanation, causes, and possible solutions
In 1961, the American mathematician William Wesley Peterson developed cyclic redundancy checking (CRC) to reduce errors occurring when transmitting and storing data. In this procedure, redundancies are added to each data block in the form of an additional test value. This value, also known as the CRC value, makes it possible to detect errors that have occurred during transmission and storage and would ideally correct them automatically.
If the cyclic redundancy check encounters at least one problematic file, a CRC error may occur that prevents the scheduled data storage or transfer from being executed. This can occur especially when downloading and extracting compressed files and archives. However, it can also happen when reading and writing data to hard disks. In this article, we’ll discuss what a CRC error is and how to resolve the problem.
What is a CRC error?
A CRC error informs you that the cyclic redundancy check has detected damaged or incomplete files. In that case, the matched value of the data and the attached CRC value do not match, resulting in an aborted action (save, copy, read access, etc.) and a corresponding CRC error message. Typically, this message is as follows:
Data error (cyclic redundancy check)The CRC error often occurs when extracting compressed files and archives. A failed cyclic redundancy check may also happen when reading and writing to local and external hard disks or USB sticks as well as CDs, DVDs or Blu-rays.
What can be done to prevent a CRC error?
If you encounter a CRC error, it can be really annoying. Your go-to solutions such as rebooting the system won’t help solve a CRC error. You can’t temporarily disable the checking procedure either, which is why the affected files seem lost at first. However, depending on the context, there are different strategies to solve the problem and save your files!
CRC error: here’s how to fix it when extracting files
If you want to extract compressed files, you can use the tools installed on your operating system. Many users do opt for third-party tools such as WinZip or WinRAR for packing and extracting documents, however, which often have a much greater range of functions. If you use this kind of software yourself, you should first check whether it is still up to date when your CRC error occurs. If you have updated the program and the error persists, try to reinstall it entirely. A change of program can also be the answer to your CRC problem.
Even an incomplete or incorrectly executed download can quickly lead to problems like a CRC error. If you have downloaded the corrupted file or archive from the Internet, we recommend that you download it again.
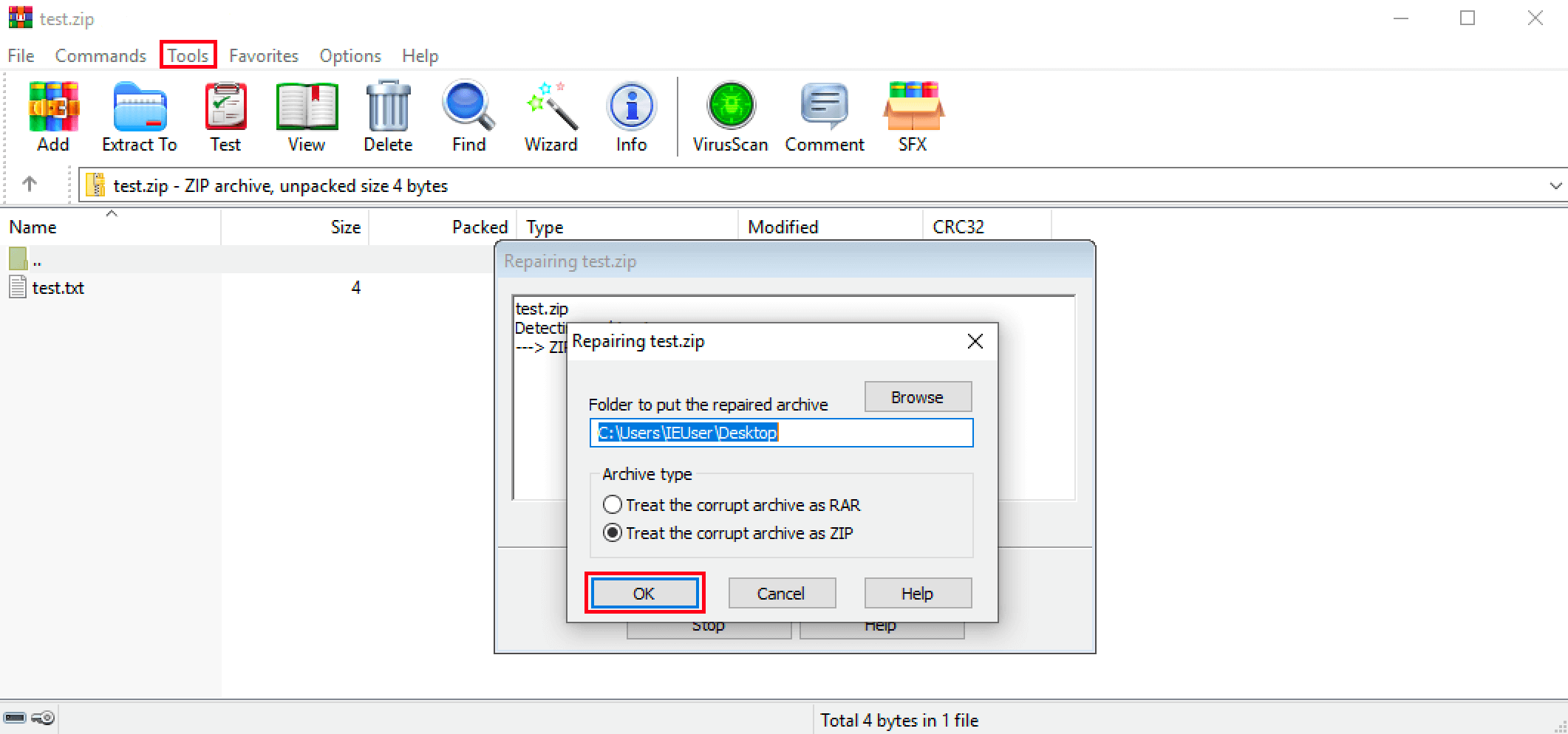
Many third-party tools can repair damaged archives or compressed files. If your program offers this option, you can try to fix the CRC error this way in the last step. For example, in WinRAR, you can start the repair as follows:
- Open the zipped file in WinRAR.
- Click on the “Tools” item in the upper menu bar.
- Select “Repair archive”.
- Specify a location for the archive to be repaired and specify the compression type (ZIP or RAR).
- Confirm to begin the repair.
- When the process is complete, there is a rebuilt variant of the archive in the defined target directory, which should not cause a CRC error during extraction.
Extracting a file despite a CRC error (using WinRAR)
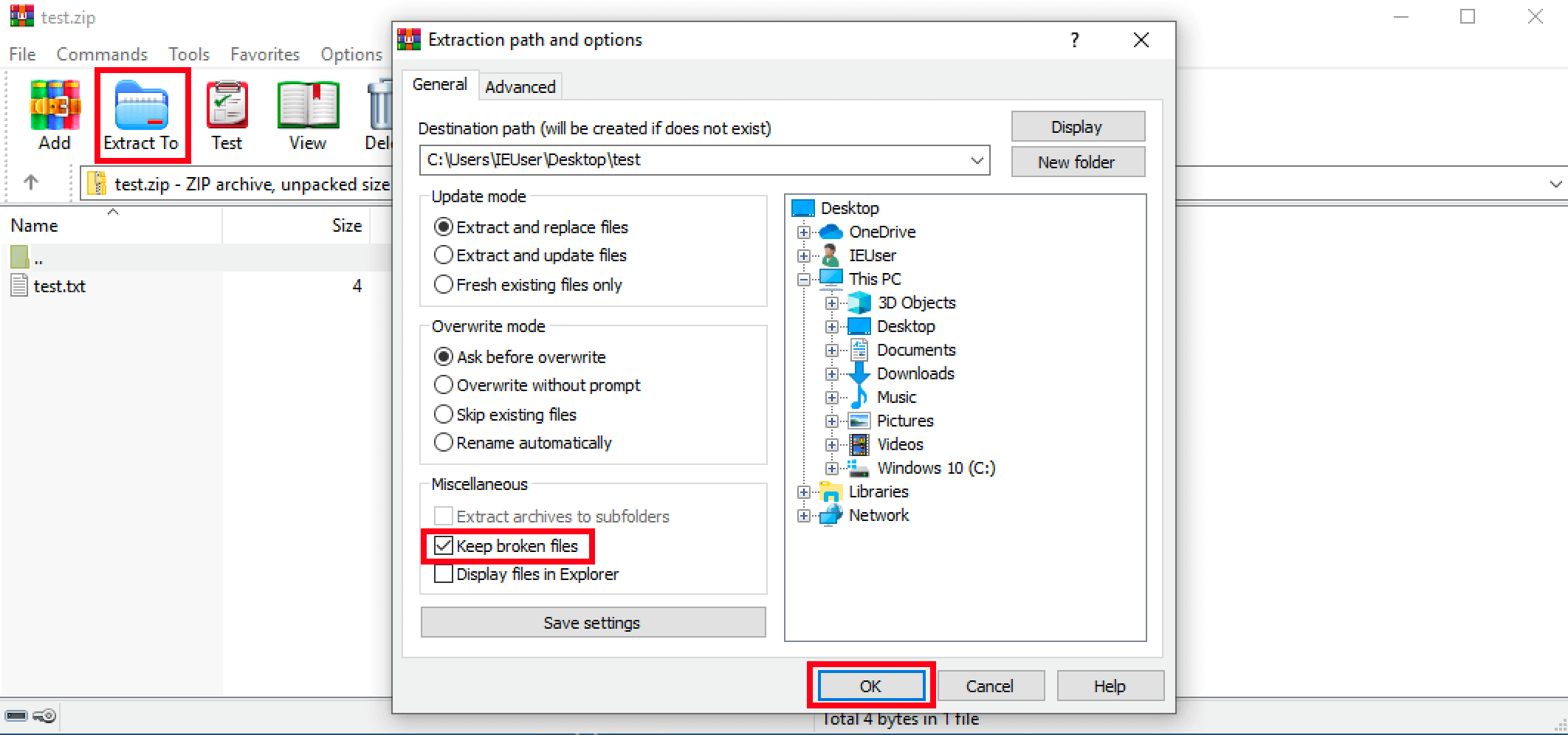
If a compressed file can no longer be extracted due to a CRC error, often most of the data is fine, and only a few files are corrupted. You could save the uncorrupted files even if you can’t fix the CRC error entirely. As an example, the following instructions show how this procedure works in WinRAR:
- Open the affected archive with WinRAR.
- Press the menu item “Extract to”.
- Mark the option “Keep broken files” in the “Miscellaneous” section.
- Confirm to finish this step.
- The files will then be extracted to the defined target directory - including the broken file(s). However, these files cannot be opened or edited.
CRC errors during read or write processes - possible solutions
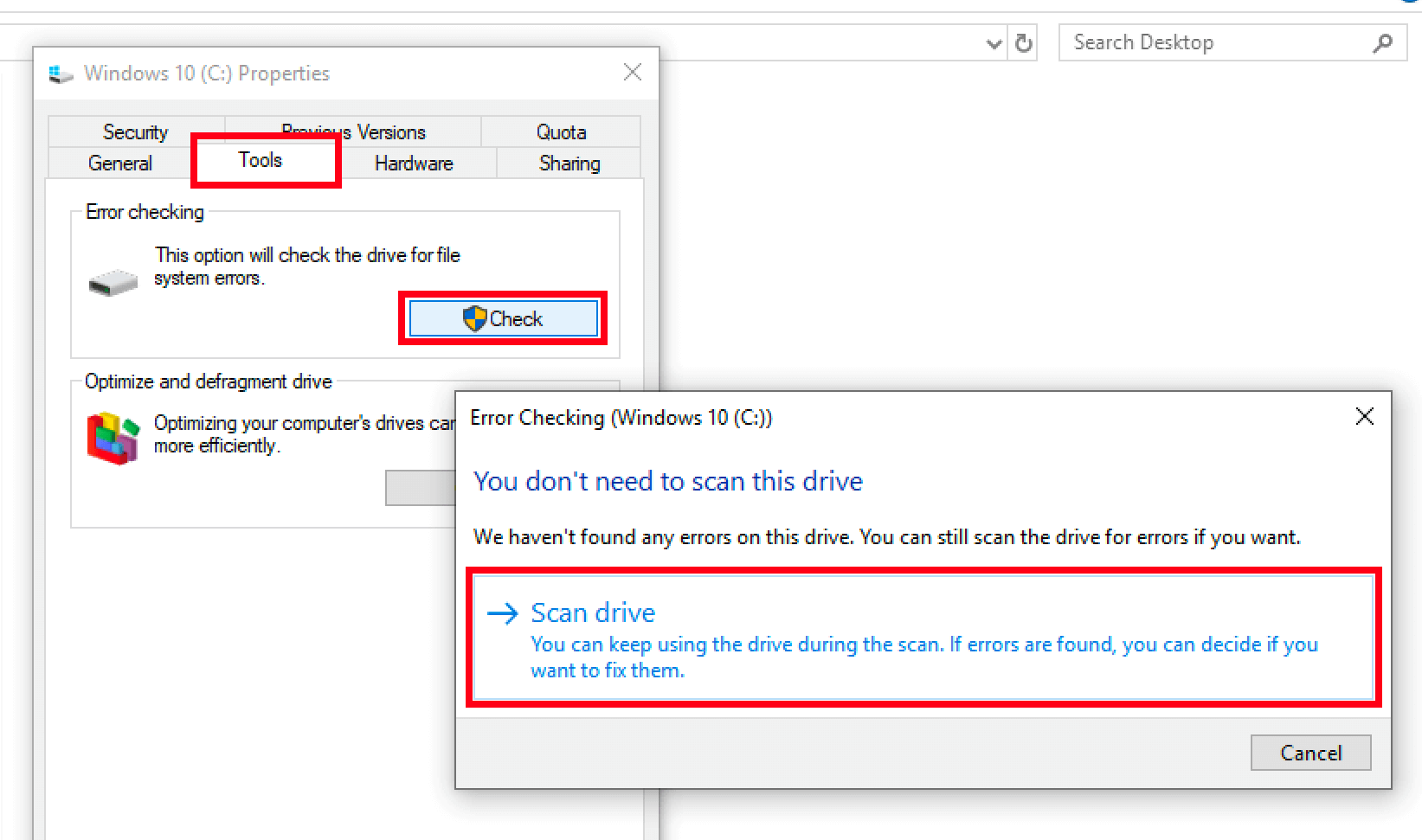
Because there is no specific troubleshooting for storage media errors, tools for general error checking of the affected media have the best chance of success. As with WinRAR, you can choose between third-party software (usually for a fee) and tools that are already integrated in your system. In Windows operating systems, the tool can be found under “error checking”. This comes preinstalled. It can be used in the following way for data problems, such as a CRC error:
- Open the File Explorer and select the problematic disk drive by right-clicking on it.
- Select the menu item “Properties”.
- Switch to the “Tools” tab.
- Click on the “Check” button under the “Error checking” options.
- Finally, press the “Scan Drive” button to start the error check.
Can CRC errors be avoided?
Problems with extraction or reading and writing of files are particularly serious if the files are required urgently. The fundamental question is whether it is possible to prevent errors resulting from the cyclic redundancy check in the first place. However, there is no proper answer in this case, unfortunately. Files or archives can be damaged at any time. However, you can make an effort to keep software for handling files up to date by regularly checking for available updates and installing them.
In addition, you can generally minimize the risk of hardware problems by always shutting down your device properly and disconnecting external hard drives and USB sticks using the “Safely Remove Hardware” feature.