SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) – the reliable, message-oriented transport protocol
The internet protocol family forms the basis so that systems can communicate in networks like the internet. There are more than 500 different members who take on mostly different roles, but there are also protocols that have more or less the same function. For example, both TCP (Transmission Control Protocol) and UDP (User Datagram Protocol) define how data is exchanged between network participants. However, while TCP requires an existing connection for this, UDP enables the connectionless transfer of files. With SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol), the IETF (Internet Engineering Task Force) published another protocol in 2000 that combines the properties of TCP and UDP.
What is SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol)?
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol, SCTP for short, is a reliable network protocol of the internet protocol family, which was designed by the IETF working group Signaling Transport (SIGTRAN). A first version of the protocol is defined in the RFC 2960 published in 2000 – seven years later the IETF published a revised version in RFC 4960. SCTP is primarily described in these standards as a protocol used to map telephony infrastructure in IP networks. In addition, it is also used in other areas, like reliable server pooling (administration of server pools for load balancing).
SCTP (Stream Control Transmission Protocol) is a reliable transport protocol of the internet protocol family that enables the transmission of telecommunications messages over IP networks. It combines several features of the TCP (connection-oriented) and UDP (connectionless) protocols, which are also responsible for data transfer, and includes mechanisms for congestion control and for improving error tolerance when sending packets. Thanks to its high flexibility, SCTP is also used in other applications (e.g. the management and administration of server pools).
What are the characteristics of SCTP?
SCTP typically uses IP as a base, but can also be based on any other connectionless packet service. The transport of packets is characterized by the following features:
- Confirmed transmission of user data (error-free and without duplicates)
- Data fragmentation to maintain the maximum packet size of each network path
- Sequenced delivery of user messages within multiple data streams (multi-streaming) – including the option to specify the order of these messages
- Bundling (optional) of several users’ messages in a single SCTP package (chunk bundling)
- Fault tolerance at network level thanks to multi-homing (host with several valid network addresses) of one of both communication partner(s)
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol therefore focuses on secure and reliable data transmission. A strict regulation of the sequence of sent data streams is not necessary, but is possible in principle at any time. In this way, a fixed sequence for the transmission of packets with SCTP only has to be adhered to when required by the accessing application. The sent data, which can be divided into several streams, is not captured byte-by-byte but by packet – which is particularly useful for message-oriented services.
A four-way handshake (mutual authentication including connection setup) between sender and receiver ensures the security addressed, without which data transfer via SCTP is not possible. In addition, the header contains a verification tag and an optionally unstable checksum field.
How the individual features of the SCTP protocol work
To clarify the functionality of the data transport through the Stream Control Transmission Protocol, we will take a closer look at the most important functions of SCTP – from the four-way handshake, to fragmentation, to the transmission of the packets.
SCTP connection setup and removal
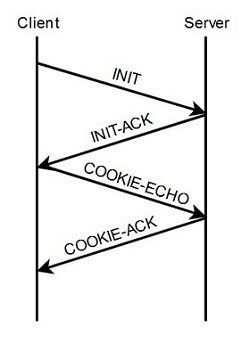
Like TCP, SCTP is above all a connection-oriented protocol, which requires an existing connection between client and server so that they can exchange data packets. To establish such a connection, both sides carry out a so-called four-way handshake, which the client initializes with an INIT request. The server responds to this request with an INIT-ACK message containing, in addition to the confirmation, a cookie uniquely identifying the proposed connection. This cookie in turn sends the client back to the server in a COOKIE-ECHO request, whereupon the latter completes the connection by means of a COOKIE-ACK message.
Established SCTP connections can either be closed by the application or the user as soon as the transfer has ended, or they are prematurely interrupted as a result of an error. In addition, it is also possible to terminate the connection at any time by request. In any case, the data transfer is completely stopped as soon as a participant disconnects.
Sequenced transmission in streams (data streams)
The term stream in the SCTP standard refers to a sequence of user data exchanged between server and client. A single SCTP connection allows any number of streams, whereby the user can specify the exact number when establishing the connection. While the order of data within a data stream is strictly adhered to, there are no fixed hierarchies and no dependencies when delivering the different streams. So, if there are problems with the transmission of a data stream, this has no effect on the transfer of the other streams. In addition, there is a mechanism by which to bypass the sequences transmission and send prioritized message packets.
While SCTP streams identify a sequence of user data, a stream in TCP connections is always a particular sequence of bytes.
Fragmentation of user data
SCTP offers the option of fragmenting packets in order to comply at any time with the path maximum transmission unit (PMTU), i.e. the maximum packet size that can be transmitted over the respective connection path. At the time of receipt, the individual fragments are reassembled and forwarded to the user as a complete message. Compared to the network-level fragmentation performed by the IP protocol, such fragmentation at the transport layer has some advantages: for example, it relieves the burden on the routers responsible for fragmenting the IP packets. It also eliminates the problem of having to resend entire messages due to a single fragment lost in the network.
Package confirmation and overload control
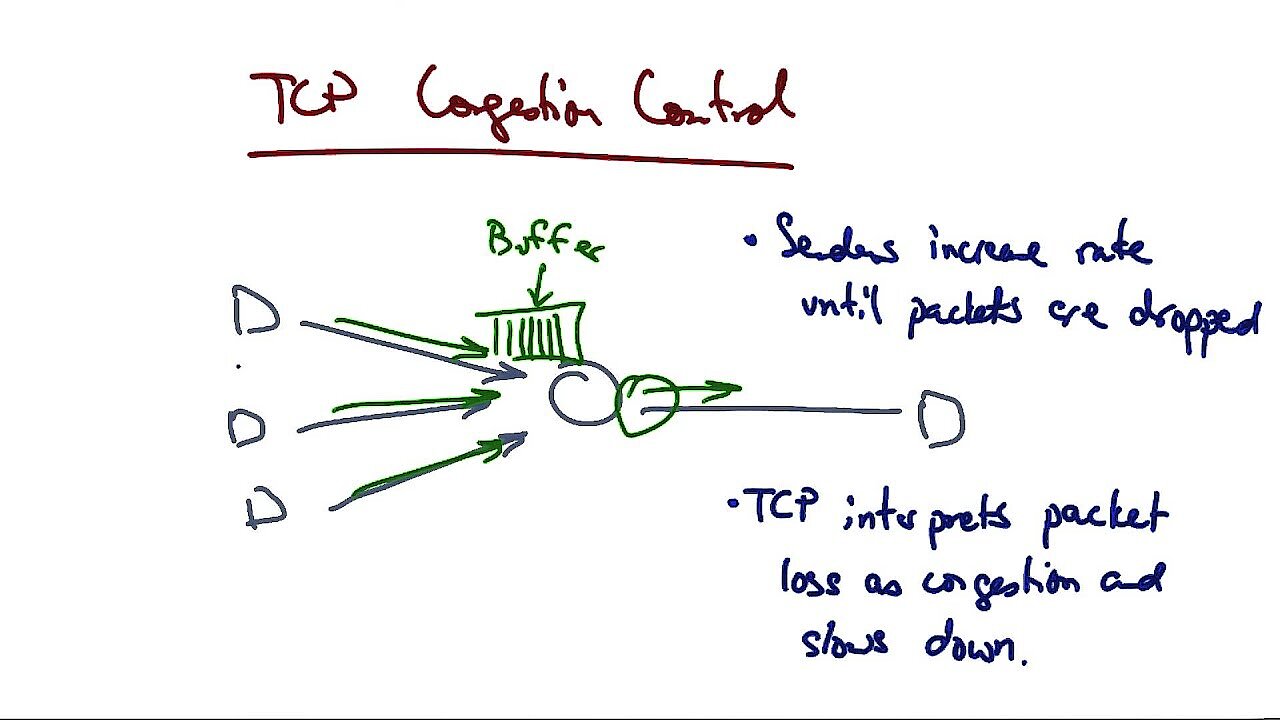
The Stream Control Transmission Protocol identifies all data fragments or unfragmented messages with a so-called transmission sequence number. For each of these sequence numbers, the sender expects an acknowledgement message from the receiver. If this does not happen within a specified period, the corresponding package will be resent. In order to be able to ensure this transmission reliably and independently of the sequenced transmission, the receiver acknowledges receipt of a transmission sequence number even if there are gaps in the transmission sequence. To ensure that the transmission is not only reliable but also as fast as possible, SCTP uses similar congestion control algorithms as TCP. These regulate the shipping so that it does not come to a congestion of the packages and thus an overload of the host.
Chunk bundling (bundling multiple messages in a single SCTP packet)
SCTP allows you to bundle multiple messages in a single package. In this way, several bits of control information and/or user data, which are also known as chunks in the SCTP standard, can be sent under a common header. The chunk bundling mechanism is responsible for both assembling and disassembling the complete package on the receiver side.
Package validation
When establishing an SCTP connection, the two endpoints negotiate a verification tag that must be specified in the packet’s headers sent during the entire transmission. If one of the communication partners receives a packet without this indicator, it discards the corresponding packet immediately. In this way, the protocol provides protection against unauthorized access and also prevents packets from previous connections from continuing to be received.
To additionally protect the data, the sender has the option of adding a CRC32C checksum to the header. The protocol provides an optional 32-bit field for this purpose.
Path management
Since SCTP supports multi-homing, users can specify a complete set of transport addresses that can be used as potential destinations for the packets sent. If multiple addresses are listed, the protocol uses the primary address path by default. If the primary address path cannot be reached, the alternative addresses are selected so that transmission can continue without interruption. To provide this service, the Streaming Control Transmission Protocol has implemented a path management function that uses the specified address instructions. It also monitors the availability of all defined address paths by regularly sending so-called heartbeats (control signals) to them.
Path management and package validation always take place at the same time.
The advantages of Stream Control Transmission Protocol
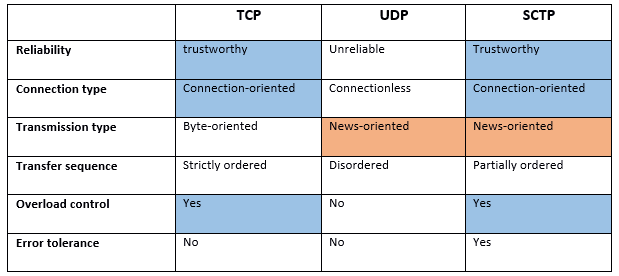
As protocol of the transport layer, SCTP competes especially with the already mentioned protocols TCP and UDP. However, an overview of the implemented functions and properties of SCTP shows that it does not replace either protocol, but rather combines them. The following table summarizes in what aspects the Stream Control Transmission Protocol is more similar to the TCP protocol and in which points it is more similar to the UDP protocol:
There are three important similarities between TCP and SCTP: Both protocols require a connection between the communication partners, offer a mechanism for overload control, and are also reliable – so they both ensure that the packets arrive at the recipient without a loss. UDP does not provide this kind of guarantee due to a lack of confirmation messages. In return, however, UDP saves the user application from having to set its own data record markers (to mark packet boundaries), since it is not byte-oriented but message-oriented – an advantage that SCTP also offers.
Apart from this flexibility, which makes SCTP the ideal solution for voice transmission services like VoIP (Voice over IP), the protocol also scores points with the support of multi-streaming and multi-homing (fault tolerance instead of alternative hosts), which neither UDP nor TCP offer. In addition, the Stream Control Transmission Protocol, with the four-way handshake (including authentication cookie), and the mandatory verification tag in the header of each packet sent, ensures the highest security convenience of all three transport protocols.