What is a broadcast address?
The broadcast address can be used to send data packets in IP networks to all participants of a local network. The individual addresses of each party in the network do not have to be known for this to work. If necessary, the broadcast address can be calculated quite easily.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
What’s behind the broadcast address?
Each network or subnet has a reserved broadcast address that can be used by all participants of the network to send a broadcast. Broadcasts allow information and services to be transmitted to all devices and components of the network without the need to know their individual IP addresses. Among other things, routers in a local area network use the broadcast IP to send HELLO packets to all endpoints, switches, and other routers to maintain interrelationships on the network and discover neighboring devices.
Broadcast: a multipoint connection in IP networks that automatically reaches all nodes in the network without knowing the recipient addresses. For this purpose, a fixed reserved broadcast address exists in each network or subnet.
How is the broadcast address calculated?
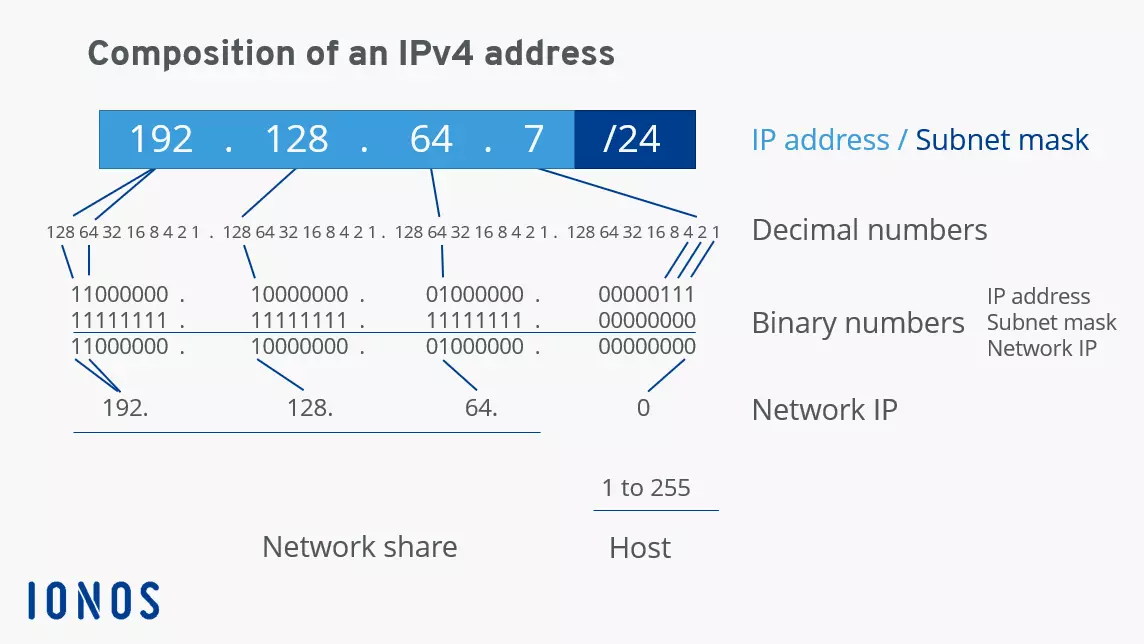
Each IP address consists of 4 decimal numbers — so-called octets — separated by dots. An octet contains 8 bits, which is why every IPv4 address is automatically a 32-bit address. Each octet can represent a number between 0 and 255. The broadcast address is always identified in the final part of the host part of an address (starts in the third or fourth octet): If all host bits are set to the binary value “1”, this is the broadcast address.
If all host bits are set to the value “0”, this is the subnet address.
The following example is intended to clarify the composition of the individual components of an IP address, including the calculation of the broadcast address:
192.128.64.7/24In each network, a broadcast IP is assigned only once. It is always the last IP address of the subnet. The broadcast address — where all host bits are set to “1” as already mentioned — is therefore: 192.128.64.255 in this example.
How to find out the broadcast IP
You want to find out the broadcast address of your network? For this, common operating systems with native command line applications and the network program ipconfig (Windows) or “ifconfig” or “ip” (Linux, macOS) provide the appropriate tool set.
In Windows, for example, proceed as follows:
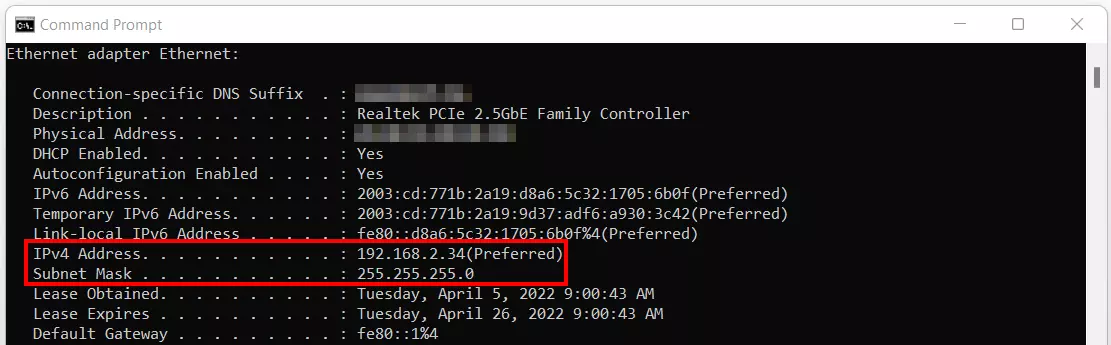
- Start the command prompt by using the key combination [Windows] + [R] and execute the command “cmd”.
- Enter the CMD command “ipconfig /all” into the command line tool to get an overview of all important key data of your local network.
Among other things, the prompt presents you with your device’s IP address and subnet mask. You can derive the broadcast IP from this information. In our example where the IP address is 192.168.2.34 and the subnet mask is 255.255.255.0, the broadcast address is 192.168.2.255.
How exactly you find out the broadcast address in Linux and macOS depends on the available network tool of the respective distribution or version. In Ubuntu 20.04, for example, you can proceed as follows:
- Open the “Show applications” menu.
- Search for “Terminal” and start the application by double-clicking on it.
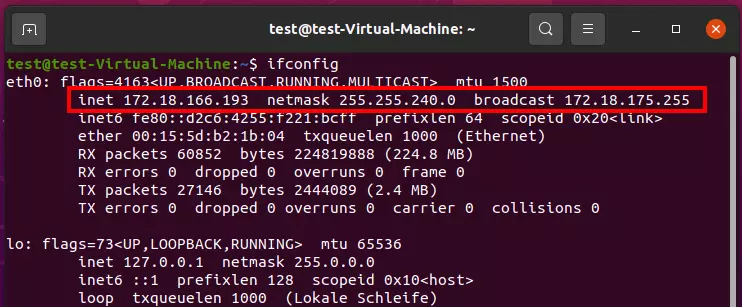
- Enter the command “ifconfig”.
Right in the second line, Ubuntu presents three values after executing the command:
- inet: the Internet address of your device (here: 172.18.166.193)
- netmask: the subnet mask of the local network (here: 255.255.250.0)
- broadcast: the broadcast address of the local network (here: 172.18.175.255)