What is an SPF record and how to check it
The Sender Policy Framework (SPF) can be used to determine whether an email is actually coming for the person whose name appears as the sender. This authentication method allows mail servers to verify the authenticity of sender addresses. You can do this yourself by checking the SPF record.
Why do email addresses need to be verified?
In theory, checking incoming emails is simple, because the inbound mail server knows the domain of the sender. For example, when an email arrives from john.doe@gmx.com, the recipient can find out the IP address of gmx.com. This address is 213.165.64.8 and can be found in the mail header along with the sender’s IP address.
However, at big companies, there’s never just one mail server. For example, the email provider gmx.com uses over half a dozen different servers. Furthermore, many large providers use specialized email filtering servers (such as mailchannels.com) to prevent spam emails from being sent through their systems. In this case, the recipient will see the IP address of the email filtering server, not that of the actual sender.
This means the recipient needs a way of knowing which IP addresses belong to the real sender. In other words, the recipient has to verify whether the sending mail server (whose IP address appears in the mail header) is truly sending the email on behalf of the sender. SPF is currently the most common method of verification.
What is SPF (Sender Policy Framework)?
SPF stands for Sender Policy Framework. This method allows mail servers to verify whether an email they receive is actually from the specified host server. This SPF check runs automatically in the background without you having to do anything.
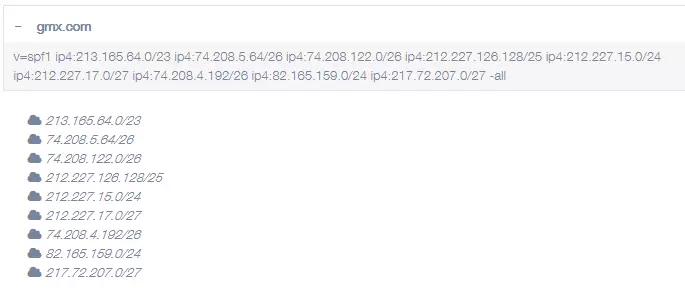
Put simply, the SPF determines which mail servers are allowed to send mail for the domain. The mail servers are identified by their name or their IP address. For example, an email from john.doe@gmx.com may only be sent via one of the following IP addresses: 213.165.64.0, 74.208.5.64, 74.208.122.0, 212.227.126.128, 212.227.15.0, 212.227.17.0, 74.208.4.192, 82.165.159.0, 217.72.207.0. These IP addresses are therefore listed in the SPF record for the domain gmx.com. The incoming mail server can then check whether the IP address that it reads in the header of the mail is on this list or not.
The list of authorized mail servers is stored on the domain name server (DNS) of the sending domain (gmx.com in this example) and can be accessed by any incoming mail server.
Reach out in your name every time you hit send — includes domain, 2 GB+ storage, and more.
What is an SPF record?
The SPF record is entered as a DNS record (a TXT record, to be exact) in the domain zone of the DNS (name server) associated with the domain. The record contains a list of IP addresses that are allowed to send emails from this domain. It also includes other records, such as records for the email filtering servers that an email must pass through before it reaches the recipient. These stopping points are often entered using an include statement. The most common parameters of an SPF record are explained below:
| Code | Meaning |
|---|---|
| v | Version of the record; v=SPF1 indicates the version that is currently valid. |
| ip4 | IP address; IP4 is the name of the most well-known form of the IP address. New IP6 addresses also exist, but they’re much less common. |
| -all | All other senders that are not listed here are unauthorized and should be rejected. |
| include | Indicates additional domains that you want to look up the SPF record for. |
There is also a version of -all with a tilde: ~all. This indicates that all other senders are not authorized but should still be accepted. The “soft fail” qualifier was originally introduced for testing purposes but is now used by various hosting providers.
Example: SPF record of gmx.com
Using an IONOS email account and want to set up an SPF record for your domain? Find out how to set up an SPF record with IONOS SPF in the IONOS Help Center.
How to check an SPF record
The tool from mxtoolbox is the easiest way to check whether emails that you send are verified with an SPF record:
- Send an email to
ping.tools.mxtoolbox.com. - After a short time, you’ll receive a reply from
abuse@mxtoolbox.com. - This email contains a basic response and a link to detailed results.
Note that it can take up to 24 hours for an SPF record to become active. If the SPF record check reports an error, try again the next day.
You can also check the SPF record by sending an email to yourself and checking the header:
- Send an email to yourself.
- Open the email and look at the email header or message source information. Depending on the mail client, you can do this from the View menu or by right-clicking to open the context menu.
- The SPF record is labeled “Received-SPF.”
If you currently don’t have your own email server, you can get one by using email server hosting from IONOS. Thanks to robust security measures and the use of an SSL certificate, your emails will always be optimally protected against unauthorized access.
What are the pros and cons of SPF records?
More and more internet service providers consider SPF records mandatory for security reasons. This means that any email from the incoming mail server that doesn’t have the appropriate authorization is delivered with a warning or not delivered at all.
Easy implementation is the biggest advantage of SPF records because a simple TXT record is all that’s needed. It can usually be created automatically by the service provider.
But as important as SPF records are, it’s important not to overestimate their security capabilities:
- SPF doesn’t protect against spoofing. A scammer can display a fake sender name in the email despite SPF.
- SPF doesn’t improve the reputation of the sender. Even a spammer can use SPF.
- SPF doesn’t protect against unauthorized email senders. SPF won’t work if someone sends an email through your mail server without authorization.
Typically, SPF records are used in conjunction with other security mechanisms, especially with DKIM and DMARC.