Megabyte – an explanation of the unit of digital information
IT personnel are constantly dealing with information units that indicate file sizes, the storage capacity of a data carrier, or the data consumption of processes. The megabyte, or MB for short, is a unit of measurement that comes up frequently. But despite frequent use, sometimes it’s not entirely clear what its size ratio is compared to kilobytes or gigabytes. When dealing with digital text documents, images, and email attachments, it’s helpful to know what MB means in practice and how the size can be converted into other common units of measurement such as KB or GB.
What is a megabyte?
Megabyte (MB) is a standard unit in IT and digital technology that designates a file size or the capacity of a data storage medium. The term is made up of the Greek word “mega” (million) and “byte”. A byte is the smallest data quantity that a computer processes when storing and processing data. But what is a byte made of? A byte is made up of 8 bits, also called binary digits. These form the basis for binary communication between computers. A single bit describes one of two states: “0” or “1”.
If you combine several bits, the number of states that can be written also increases. With one byte, i.e., 8 bits, 256 (28) states are possible. Nevertheless, a byte is just large enough to represent a single character. This example shows that complex digital processes and representations require a huge number of bytes. To keep a better overview, bytes are therefore grouped into different size units. According to the decimal system, a megabyte stands for 1 million bytes. 1 MB is a lot easier to write than “1,000,000 bytes”.
While a byte with its 8 bits represents the smallest addressable IT unit, there are designations for units that are even smaller. A half-byte or nibble consists of 4 bits and half a nibble, i.e., 2 bits, is a dibit.
Megabyte, kilobyte, and gigabyte – what’s the difference?
So, what’s larger – a MB or a GB? And what is the difference between KB and MB? There are always confusions when it comes to digital storage units. The correct classification of kilobytes, megabytes, and gigabytes makes it easier to deal with files and storage carriers. According to the decimal system, 1 megabyte = 1,000 kilobytes and 1,000 megabytes correspond to one gigabyte. 1 MB is therefore significantly larger than 1 KB and significantly smaller than 1 GB. However, because the prefixes kilo, mega, and giga are based on the decimal system and computers use the binary system, this conversion is not accurate.
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) found a solution to this problem. It introduced new prefixes that weren’t based on the power of ten but on the power of two which are used by computers. These prefixes are based on their decimal counterparts but are assigned the syllable "bi". Megabyte thus becomes mebibyte, gigabyte becomes gibibyte, etc. As a result, instead of the conversion number 1,000 (103), the technically correct 1,024 (210) is used. Nevertheless, the binary prefixes have not caught on just yet. Instead, the old decimal prefixes are still widely used, but with the more precise conversion of 1,024.
What other data units are there?
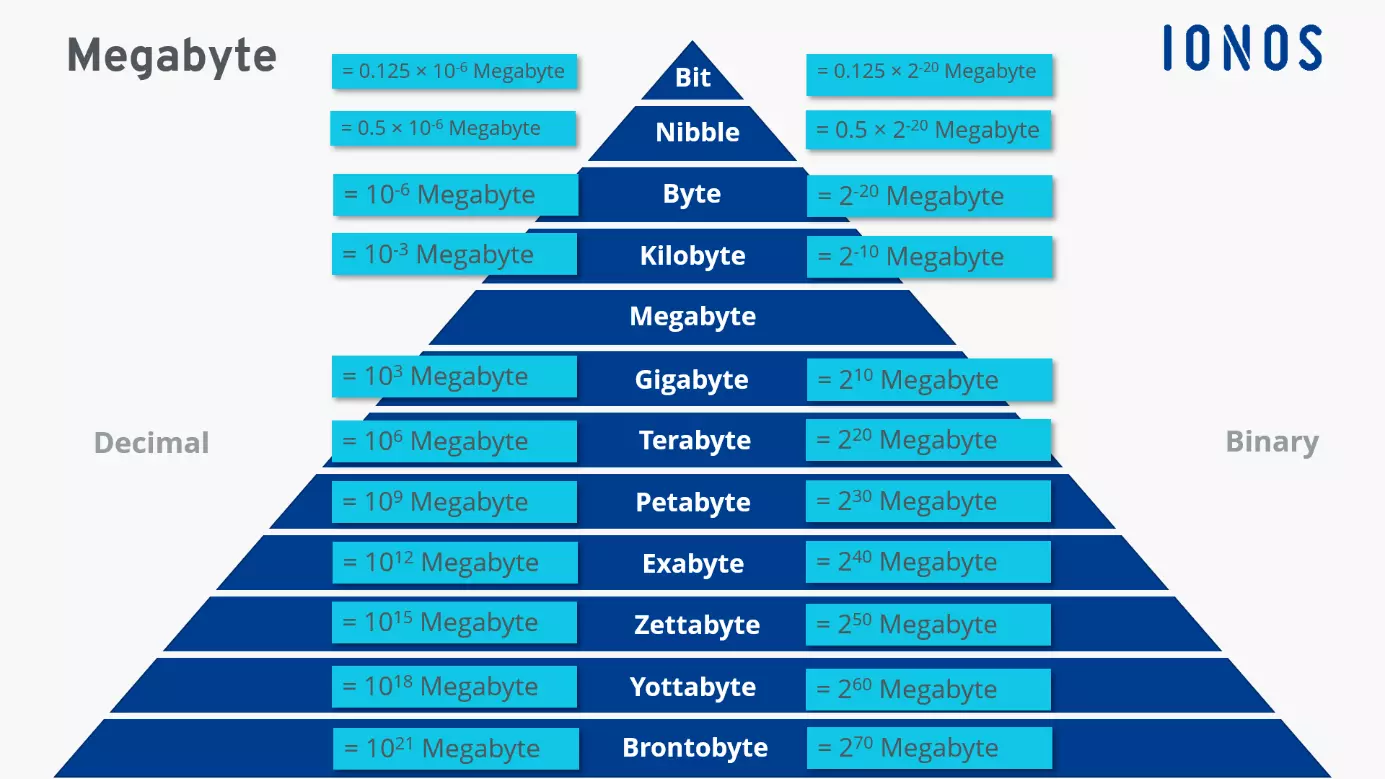
A few decades ago, the megabyte used to be a large data quantity. Nowadays, we encounter significantly larger units of measurement across digital technologies. The table below shows which data capacities are currently being used and how you can convert them to other storage sizes.
| Storage unit | Conversion | Value in byte |
| Byte (B) | = 8 Bit | 1 |
| Kilobyte (KB) | = 1,024 Byte | 1,0241 |
| Megabyte (MB) | = 1,024 KB | 1,0242 |
| Gigabyte (GB) | = 1,024 MB | 1,0243 |
| Terabyte (TB) | = 1,024 GB | 1,0244 |
| Petabyte (PB) | = 1,024 TB | 1,0245 |
| Exabyte (EB) | = 1,024 PB | 1,0246 |
| Zettabyte (ZB) | = 1,024 EB | 1,0247 |
| Yottabyte (YB) | = 1,024 ZB | 1,0248 |
| Brontobyte (BB) | = 1,024 YB | 1,0249 |
The information in the table above can seem quite abstract. To give you a better idea of what the megabyte storage unit means in everyday use of digital media, here are a few examples:
Approx. 1 MB = 500 pages of text in Word
Approx. 5 MB = 1 photo taken by a 12 megapixel camera
Approx. 30 MB = 1 minute of a YouTube video in HD quality
Approx. 500 MB = Contents on a standard CD-ROM
Approx. 5,000 MB = DVD quality film
Since when has the megabyte been used and what for?
In the age of gigabytes and terabytes, megabytes are now relatively small quantities of data. But this wasn’t always the case. In 1956, IBM launched the first computer with integrated data storage. At a price of $35,000, this huge device had a storage capacity of a mere 5 MB. A decade later, the first floppy disks with a storage capacity of up to 2 MB became available – a breakthrough for digital technologies. Nowadays, you can hardly find a USB stick with less than 4 GB of storage space.
However, this doesn’t mean that MB as a unit of measurement is now obsolete. While megabytes are no longer used in conjunction with the storage capacity of data carriers, they are used to denote file sizes. The size of digital documents, pictures, songs, or presentations is usually somewhere in the MB range. Data volumes when surfing on mobile devices and other actions that consume data are often expressed in MB. Many Internet users also know, for example, that their mail provider limits sending individual attachments over 10 or 20 MB.
Instead of using physical data carriers or their own servers, many teams and users store their data in the cloud. This allows for more flexible access and protects against data loss. The secure HiDrive Cloud storage from IONOS provides affordable packages for up to ten users, making email attachments a thing of the past.