RAID 6: Storage technology to minimize data loss
Combining multiple hard drives into a single logical drive isn’t exactly a new approach. Over the years, various setups have proven successful, and become standardized as RAID levels (Redundant Arrays of Independent Disks). One approach that is rarely used, but is relevant thanks to its high fail-safety, is RAID 6. Find out what makes RAID 6 stand out, its strengths and weaknesses and when you should use it.
What is RAID 6?
RAID 6 is a data storage approach that combines four or more hard drives into a single logical drive. Compared to individual data carriers, it boosts reliability of the system and read speeds. The basis for this is the combination of striping and parity, that also forms the basis of RAID level 5. It comes as little surprise then that RAID 6 is often referred to as “RAID 5 expansion”.
RAID 6 systems implement the “striping” approach in a classic manner. All data is divided into blocks and distributed evenly to the participating hard disks. This gives users the option of accessing several disks at the same time and reading the sub-blocks of a data strip in parallel.
When it comes to parity, RAID 6 differs from other levels: the system always saves two sets of parity information. In that way, associated data can be restored if one or two disks fail. For this purpose, a RAID 6 system can optionally use the XOR logic or a mix of XOR logic and multi-bit error correction using Reed-Solomon code. The latter is also required to transmit television signals according to the DVB standard, where it improves the bit error rate of the received signal.
XOR stands for eXclusive OR. XOR connects two statements with the two-digit junction “either ... or”. For data in a RAID 6 network, this means that during the write process, all elements of a data strip are linked with the appropriate parity information using XOR logic. If devices now access the data record, they can reconstruct the respective data using the appropriate parity block (if data is no longer available).
The total storage capacity of a RAID 6 drops significantly compared to that of individual drives. The space available for user data can be easily calculated using the following formula:
(Number of hard drives - 2) x space of the smallest hard driveFor example, with four 1GB hard disks, only 50 percent of their potential memory would be available to store user data. However, as the number of disks increases, this relationship between capacity and parity improves.
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a combination of at least two different storage media to form a single large logical drive. The specific function is determined by the respective hard drive setups, which are defined in RAID levels such as RAID 6. Its key advantages are enhanced data security and an improved data throughput rate.
Overview of RAID 6 functionality
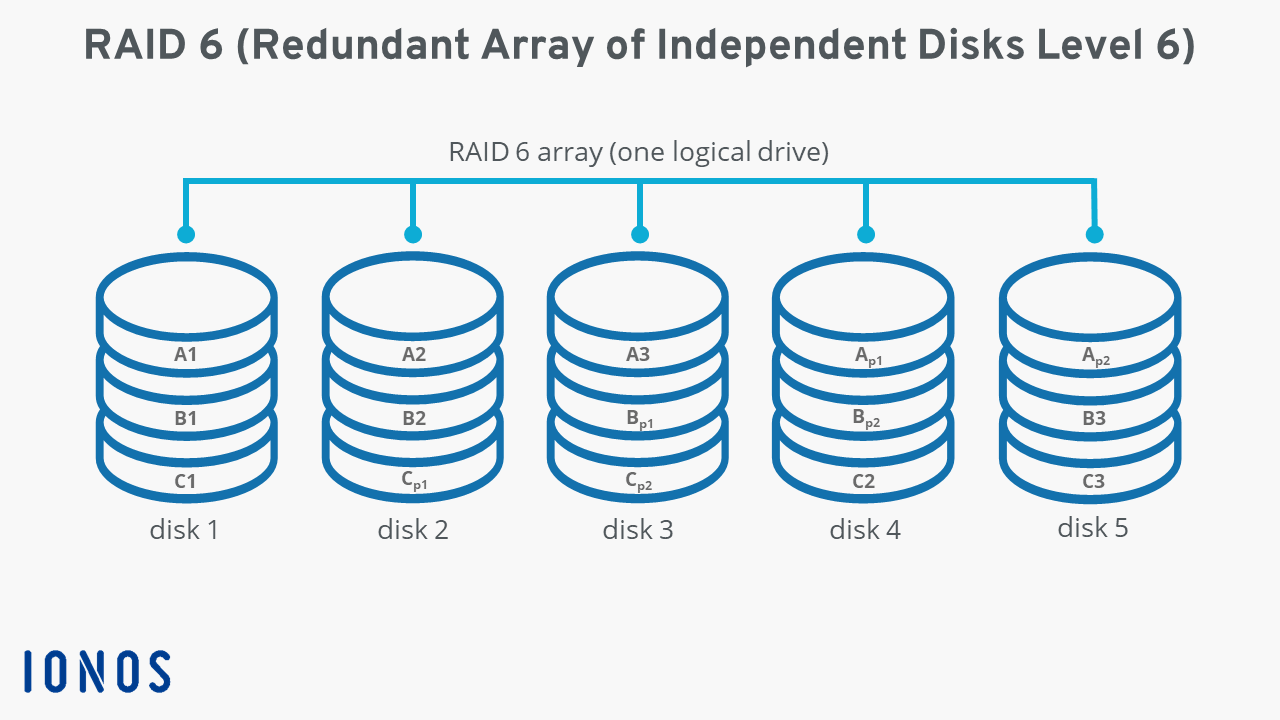
RAID 6 systems distribute all user data and parity information evenly across the integrated hard disks. This means that each disk saves the data blocks (here: A1, A2, etc.), sometimes the parity blocks (here: Ap1, Ap2, etc.) of a data stripe. The following diagram of a network with five hard disks demonstrates the functionality of RAID 6.
Pros and cons of a RAID 6 combination
Compared to RAID 5, the extended RAID 6 has one decisive advantage: parity information to recover lost data is saved in duplicate. Duplicated parity data is a more efficient way of creating redundancy, and also ensures higher reliability. In the RAID 6 system, up to two hard disks can fail at the same time without endangering the operation of the system.
The increased reliability of a RAID 6 is not synonymous with a data backup, which is why this hard drive network is never an alternative to backing up your data but acts as a supplement to a backup solution.
The advantages of RAID 6 are also closely linked to the strengths of RAID 5. The possibility of parallel access ensures a better throughput rate when reading data. Because of double parity, this advantage is weaker compared to level 5 systems. The ratio between the capacity for storing user data and no storage capacity (for parity) is weaker compared to RAID 5. However, when five hard disks are installed in a RAID 6, the system proves more resource-efficient and can be scaled with every additional hard disk.
Compared to single drives, the significant reduction in potential storage space is one of the system’s major disadvantages. This is particularly evident in a system of four disks where just 50 percent of storage capacity is available. The write performance is another disadvantage in a RAID 6 network. If data is saved on the linked hard disks, parity is calculated and distributed twice each time. This minimizes the write rate, which is evident when rebuilding the system, i.e., when integrating new hardware as a replacement for defective copies.
| Advantages of RAID 6 | Disadvantages of RAID 6 |
|---|---|
| High reliability thanks to double parity | Write speed significantly reduced compared to single drives |
| Slightly improved throughput rate in the reading process compared to single drives | The storage capacity of the individual hard disks is significantly restricted, especially in smaller networks |
When is RAID 6 used?
Because RAID 6 acts like a buffer between two possible hardware failures, its potential to store large amounts of data in a fail-safe manner long-term is huge. Ideal applications are therefore server systems where large amounts of data are archived. Database or transaction servers, which typically use RAID 5, can also benefit from a RAID 6 storage structure if the security of the data is the focus and a minimized write speed is compatible with the requirements of the respective application.
When storing sensitive data, it’s important to have a backup strategy that works. With Cloud Backup from IONOS, you can encrypt and secure your data in certified IONOS data centers!
What other common RAID levels are there?
RAID 6 is a fail-safe alternative to the more widely used RAID 5. But redundancy through parity isn’t the only option. Other standards such as RAID 1 and RAID 10 store data in a mirrored manner, i.e., always in duplicate. The latter approach combines two RAID levels with one another, in that it not only includes the mirroring technology of RAID 1, but also distributes the data according to RAID 0 to all integrated hard drives.