What is RAID 0?
RAID 0 is a permanent feature among the list of common RAID levels, even though, strictly speaking, the standard isn’t even a Redundant Array of Independent Disks. The core principle, i.e., redundant data storage, isn’t given with this level of hard drive coupling. In a RAID 0 network, which is always composed of at least two near or fully identical storage media, a single logical drive is created to optimize read and write access. Compared to other RAID levels, data security doesn’t improve with RAID 0.
- Simple registration
- Premium TLDs at great prices
- 24/7 personal consultant included
- Free privacy protection for eligible domains
What is RAID 0?
RAID 0 is a standardized RAID level that describes the combination of two or more hard drives for the benefit of performance optimization. For this purpose, all data is evenly divided into “stripes” or blocks on a participating storage media. This is also known as “striping”. Let’s look at an example. Say hard disk 1 receives data block “A1” during a write process, while hard disk 2 stores data block “A2” at the same time. Combined, the two blocks form data record “A” or a part of this data record (depending on its size). If the data is requested later, it can be read in parallel.
Experts refer to the size of the individual blocks as striping granularity or chunk size which is typically 64 kilobytes (kB).
RAID 0 uses striping to maximize both write and read speeds. However, if a hard drive fails, the data is lost because intact hard drives only have their respective stripes stored on them.
A RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) is a combination of at least two different storage media to form a single logical drive. The specific function is determined by the respective hard disk setups, which are defined in RAID levels such as RAID 0. Its key features are enhanced data security and an improved data throughput rate.
Overview of the functional principle of RAID 0
In principle, it doesn’t matter how many hard disks make up a RAID 0 array. However, the complexity and the administrative effort required to maintain a RAID increases with the number of hard drives. The operating software that links all data carriers to a logical drive is required with every additional component.
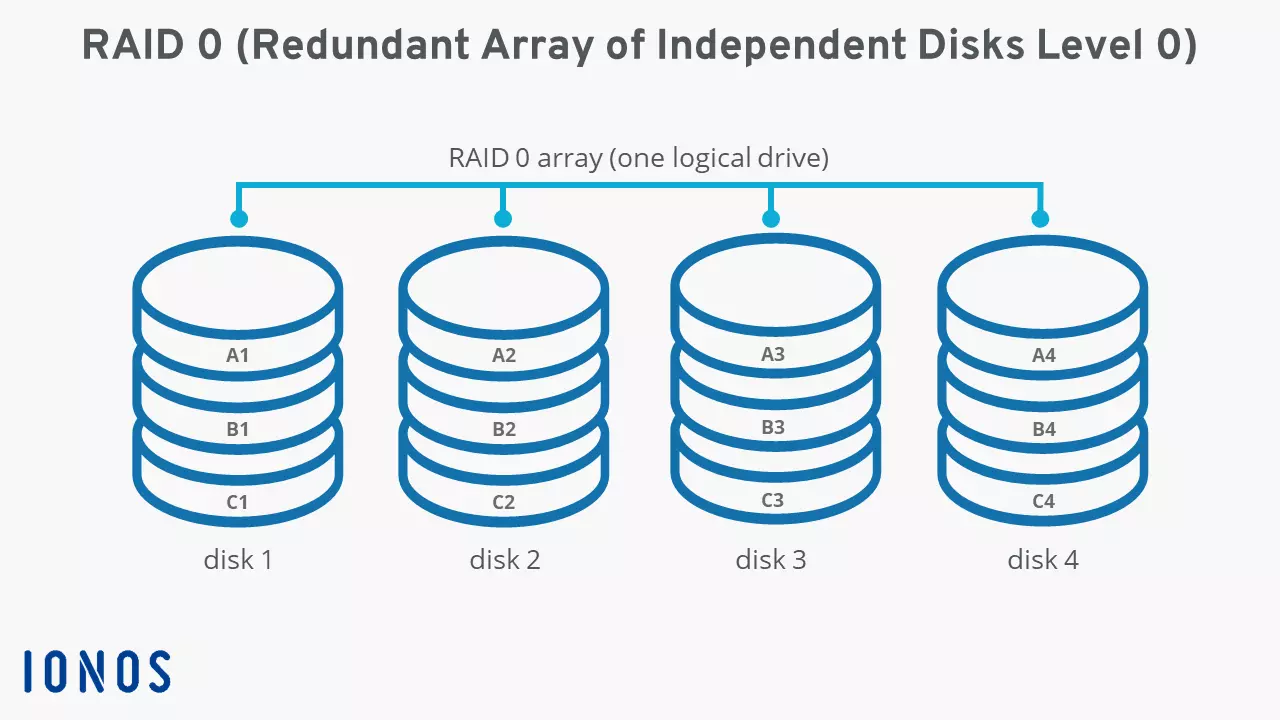
The following graphic shows an example of four hard drives combined into a RAID system. The equally sized data sets “A”, “B”, and “C” are distributed evenly; they are striped (i.e., split) to represent a quarter on each disk.
Overview of the pros and cons of RAID 0
Parallelized data access is one of the great advantages of a RAID 0 array over a single hard drive. The network provides more bandwidth, and automatically increases the number of possible input and output operations per second (IOPS for short). However, because the use of SSDs in a RAID array comes at the expense of performance, this advantage doesn’t apply to newer storage devices. RAID 0 is geared toward the use of HDD hard disks more so than other RAID levels.
A decisive disadvantage compared to a single storage medium is the higher risk of failure. Each hard disk in the network can fail on account of hardware or software problems, thereby causing the entire system to fail. Importantly, as the number of linked data carriers grows, so does the risk of total failure.
This is compounded by the fact that such a scenario is almost invariably associated with a loss of the majority of the stored data if a separate backup strategy isn’t followed. As mentioned, RAID 0 doesn’t offer any redundancy compared to other RAIDs. Following failure, striped volumes may be missing data. Individual files may be retrievable from intact storage memory in a RAID 0 system.
| Advantages of RAID 0 | Disadvantages of RAID 0 |
|---|---|
| Greater bandwidth than single drives | Higher probability of failure compared to single drives |
| Higher number of input and output operations per second compared to single drives (HDD) | A lack of redundancy means data may be lost in the event of a defective disk |
Regular backups are essential to protect sensitive and personal data from loss in the long-term. With Cloud Backup from IONOS, you can secure the data of your IT infrastructure, your smartphone, or your PC in certified IONOS data centers.
What are typical usage scenarios for RAID 0 systems?
The strengths and weaknesses of a RAID 0 system clearly show the type of projects for which this storage approach is suitable. HDDs linked to one another according to RAID 0 provide excellent performance surpassing that of individual hard disks. Non-critical applications such as software for audio or video processing, where data needs to be read and written quickly, benefit from this approach. In this case, a RAID 0 system makes for an inexpensive alternative to an SSD. As a storage setup for sensitive information such as customer data or private files, the concept is not suitable due to lack of redundancy.
What other common RAID levels are there?
The lack of a backup mechanism is unique to RAID 0. All other standardized RAID levels use methods to prevent data loss. Some approaches such as RAID 1 or the combination RAID 10 rely on mirroring of data: files are always stored on at least two different hard drives. Other modes such as RAID 5 and RAID 6 use parity information generated during the write process in order to reconstruct data in the event of a hardware defect.
Our RAID level comparison provides an in-depth overview of the differences and similarities of the most common RAID concepts.