How to fix a SMTP 550 mailbox error
The SMTP error code 550 signals that the requested action couldn’t be completed because the recipient’s mailbox is unavailable. This error belongs to the 5XX status code class, indicating a permanent issue, such as an invalid email address, insufficient access rights or a policy violation. In modern mail environments, the 550 error can also occur due to spam suspicion or authentication issues.
What are SMTP status codes used for?
To exchange messages, email servers and clients use the Simple Mail Transport Protocol (SMTP). This protocol, part of the Internet protocol suite and defined in RFC 5321, works alongside more familiar protocols like POP3 and IMAP, which are used exclusively for retrieving email once it’s been delivered.
During SMTP communication, servers send status codes to confirm connection establishment or message transfer, request further input, or indicate a disconnection. Additionally, there are error codes: temporary errors receive codes in the 4XX range, while permanent or critical failures, such as failed deliveries, are marked by 5XX status codes. For example, a mail server may return SMTP 550 (sometimes with messages like “Relay not permitted”) when it can’t deliver a message to the intended recipient.
- Personalized email address
- Access your emails from anywhere
- Highest security standards
What causes the SMTP 550 error?
According to RFC 5321, the standard format of the 550 status code is “550 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable.” This typically means the recipient address is not available. According to the IETF document, some possible causes include:
- An invalid recipient address (mailbox not found).
- Lack of permissions to use the SMTP service.
- Rejection due to policy restrictions.
- Misconfigured DMARC/SPF/DKIM (e.g. SPF check failed).
This error appears when an email client tries to send a message via SMTP, but the request fails for one of the reasons above. Whether and how the SMTP server communicates the specific reason to the client depends on the system and software in use — so while the issue is the same, the error message might appear in different forms.
What do SMTP 550 error messages look like?
The message that accompanies an SMTP 550 error can vary depending on the email provider. That’s because the basic 550 code itself doesn’t explain the cause — it only states that the request failed. If you’re troubleshooting an SMTP 550 error, it’s important to read the full message carefully. Some common variants include:
- 550 Requested action not taken: mailbox unavailable
- 550 User unknown
- 550 Mailbox not found
- 550 Relay not permitted
- 550 Recipient address rejected: User unknown in local recipient table
- 550 Reject due to policy restrictions
- 550 Invalid address
- 550 User has too many messages on the server.
- 550 Permanent failure for one or more recipients
- 550 SPF check failed


How to fix a SMTP 550 error
As shown above, the SMTP 550 error has many possible causes, so there’s no one-size-fits-all solution. Whether you can resolve the issue yourself depends on the situation. Below, we cover solutions to four common variations of the SMTP 550 error.
How to solve the authentication “550 Relay not permitted” problem
The message “550 Relay not permitted” indicates a failed connection between your email client and the mail server (some servers use SMTP 553 for this). Two common causes include either because SMTP authentication is not enabled in the client, or the stored credentials are incorrect.
In both cases, you’ll need to check and update the outgoing server settings in your email client. If you’re using Outlook, you can do this as follows:
- Go to the Control Panel, then select Mail (Microsoft Outlook).
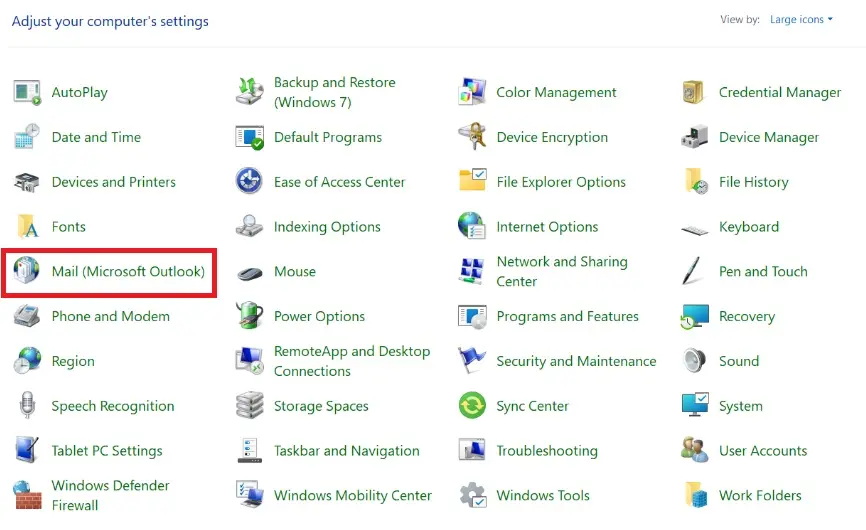
- Click on E-Mail Accounts, choose your mailbox, then click Change to access the POP and IMAP account settings. However, you don’t need to make changes here. Click on the More Settings button to open the Internet E-Mail Settings menu.
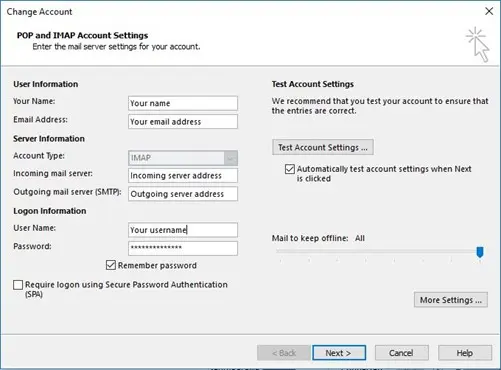
- In the Outgoing Server tab, check the box labeled My outgoing server (SMTP) requires authentication. Also select Use same settings as my incoming mail server so Outlook can operate with the usual login details. If authentication was already enabled, but uses different credentials, switching to this default login option may resolve the issue.
How to fix the “550 requested action not taken mailbox unavailable” message
This variation of the SMTP 550 error usually indicates that the recipient address cannot be reached. In such cases, the first thing to check is the address itself – often, a simple typo or mistake while creating the email is to blame. However, the issue can also be on the recipient’s end. It might occur if the recipient’s address is temporarily unreachable due to a technical issue or if the mailbox has been deactivated or deleted.
If possible, contact the recipient by another method to confirm the correct address or ask them to reactivate their mailbox. If that’s not an option, try resending the message later — the recipient may become reachable again.
How to fix the “550 reject due to policy restrictions” message
This error means that some aspect of the email violates your provider’s sending policies. The most frequent causes are:
-
Your email address has been flagged as a spam source, leading to blocked delivery.
-
The sending server address isn’t a Fully-Qualified Domain Name (Fully-Qualified Domain Name).
If the issue is the domain name, ensure the server uses a complete and valid FQDN. If your address is suspected of spam, check it using tools like the Spamhaus Blocklist Removal Center.

Enter the domain and click Lookup. The tool checks against the Spamhaus database of known spam sources and tells you whether you’re listed or not.
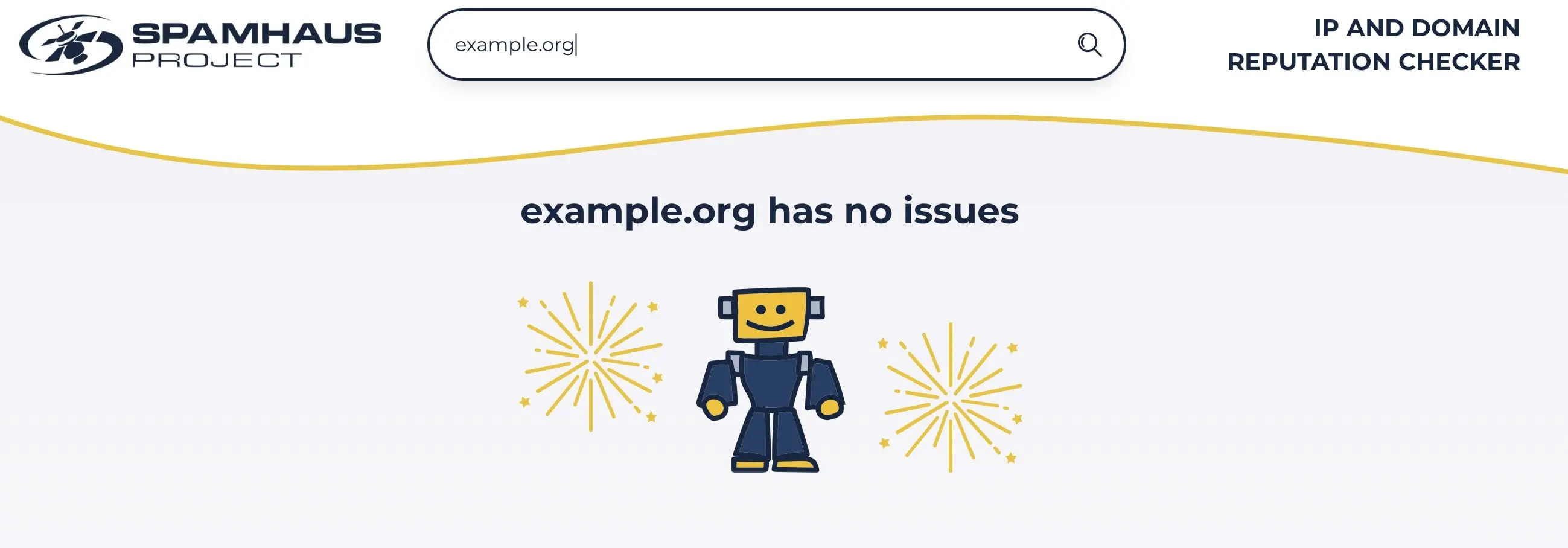
If you are listed, contact your email provider immediately to resolve the issue together.
How to fix the “550 SPF check failed” message
This error means that the recipient’s mail server checked your message against the SPF record of your domain and found that the sending server wasn’t authorized to send emails on behalf of the domain. SPF is a DNS-based mechanism that allows domain owners to specify which servers are authorized to send emails on their behalf. Since May 5, 2025, major providers like Microsoft have enforced SPF, DKIM, and DMARC checks more strictly. If an email is sent from a server not listed in the sender domain’s SPF record, the receiving server may reject it with the error code 550 5.7.15.
To fix the SMTP 550 error:
- Check your SPF record using MXToolbox SPF Lookup to verify if the sending server is listed in your domain’s SPF zone.
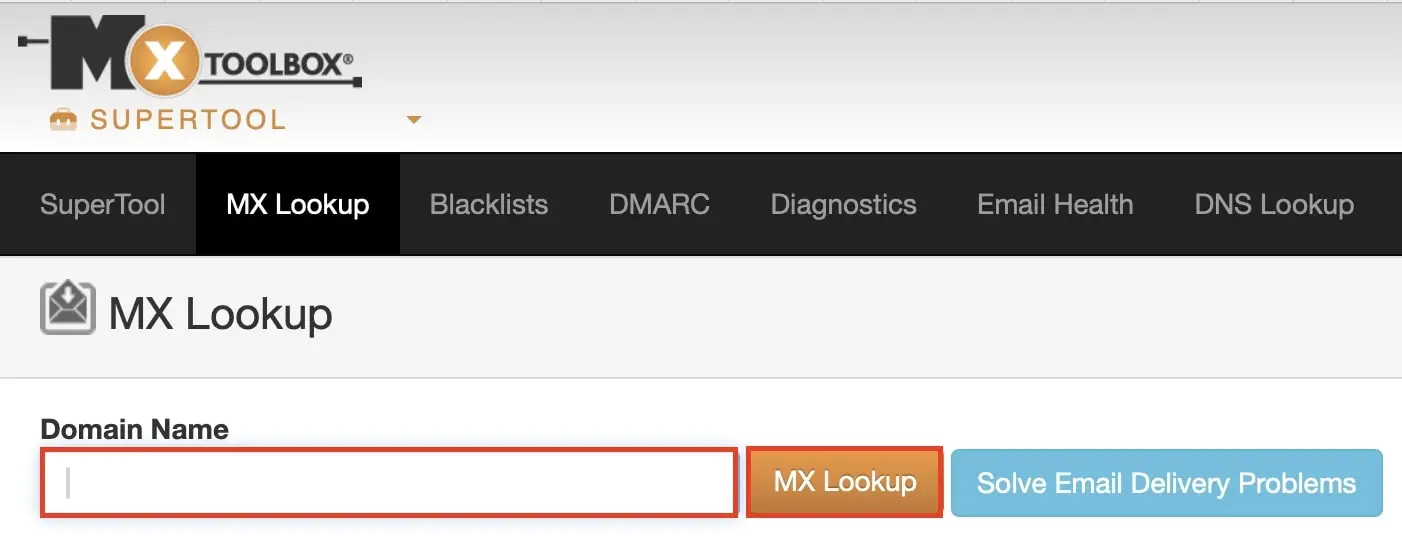
- Update your SPF record if your sending server is not listed. Here is an example SPF entry for IONOS:
v=spf1 include:_spf.perfora.net include:_spf.kundenserver.de ~allNote that DNS changes may take 24 to 48 hours to take effect globally.