How to install TYPO3 step by step
TYPO3 is a powerful and free open-source content management system that can be used across platforms. With countless extensions and templates, TYPO3 offers flexible design options for both small websites and large, multilingual projects. However, installing and tailoring TYPO3 to specific needs usually requires a certified TYPO3 service provider. Do you want to install TYPO3 yourself and need a detailed guide? Simply follow this step-by-step tutorial.
Prerequisites for installing TYPO3
Installing TYPO3 doesn’t require additional software. However, you might need an FTP program for file transfer. Most TYPO3 hosting providers include this pre-installed on their servers. A basic requirement is a web browser with JavaScript and a web server like Apache, NGINX, or IIS.
The TYPO3 development team currently supports two versions, which are TYPO3 13 and TYPO3 12 LTS. Below are the minimum requirements for the current secure versions:
- A web server with PHP version 8.1, 8.2, or 8.3 (TYPO3 12) or PHP 8.2 and higher (TYPO3 13).
- A SQL-based database compatible with Doctrine DBAL, such as MySQL version 8.0.17 or later, MariaDB 10.3+, PostgreSQL 10.0+, or SQLite 3.8.3+.
- At least 256 MB RAM (more is recommended, depending on the size of the website).
- PHP configuration with a minimum of 128 MB memory limit (Apache, IIS, NGINX).
- For image processing, the team recommends the GraphicsMagick and ImageMagick libraries.
How to install TYPO3 step by step
TYPO3 is platform-independent and available as open-source software. Providers often offer TYPO3 pre-installed as part of their hosting plans. If you want to configure TYPO3 to your exact specifications, the Source Package gives you the freedom to do so. Experienced TYPO3 developers can directly modify the source code, and over a thousand extensions support customization.
In this example, we are using a Windows operating system and the FTP program FileZilla. We will download TYPO3 version 12 LTS from typo3.org.
Step 1: Visit the TYPO3 download page, where you’ll find the latest releases of supported TYPO3 versions. Developers highlight the main differences between the versions. Choose the version that suits you best. For instance, to install TYPO3 12, click Get Version 12, which will take you to the download page.
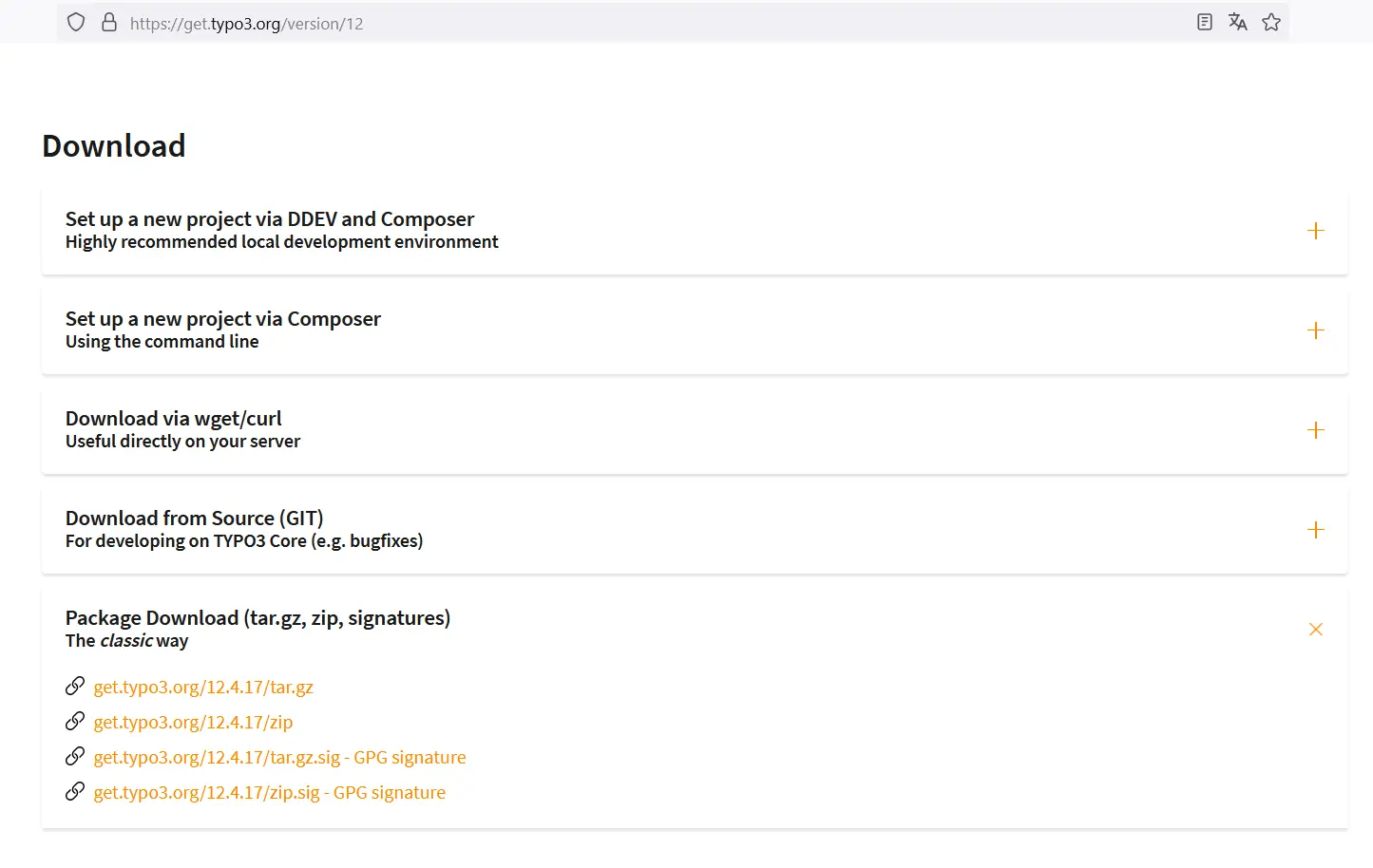
Step 2: To demonstrate the classic method, we download TYPO3 as a compressed .tar file. This solid tar compression is suitable for Unix/Linux systems. Windows users should download the .zip file. The GPG-signed packages (at the bottom of the page) ensure the authenticity of the downloaded program. This version is recommended for professional users.
Step 3: Click on the corresponding link to start the download. Once it’s completed, click the download arrow in your browser window.
Step 4: Select the file, and it will open as a compressed archive for installing TYPO3 in your extraction program.
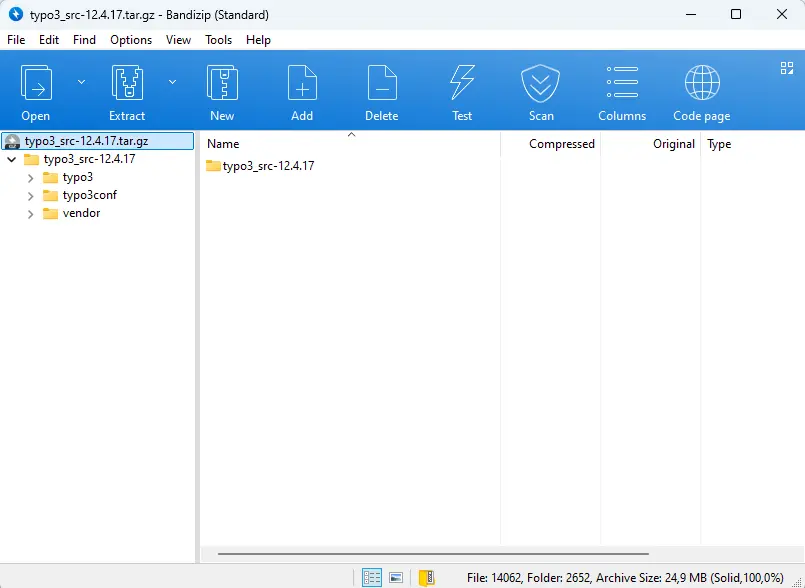
Step 5: Extract the entire folder and save it to a directory you can easily locate later.
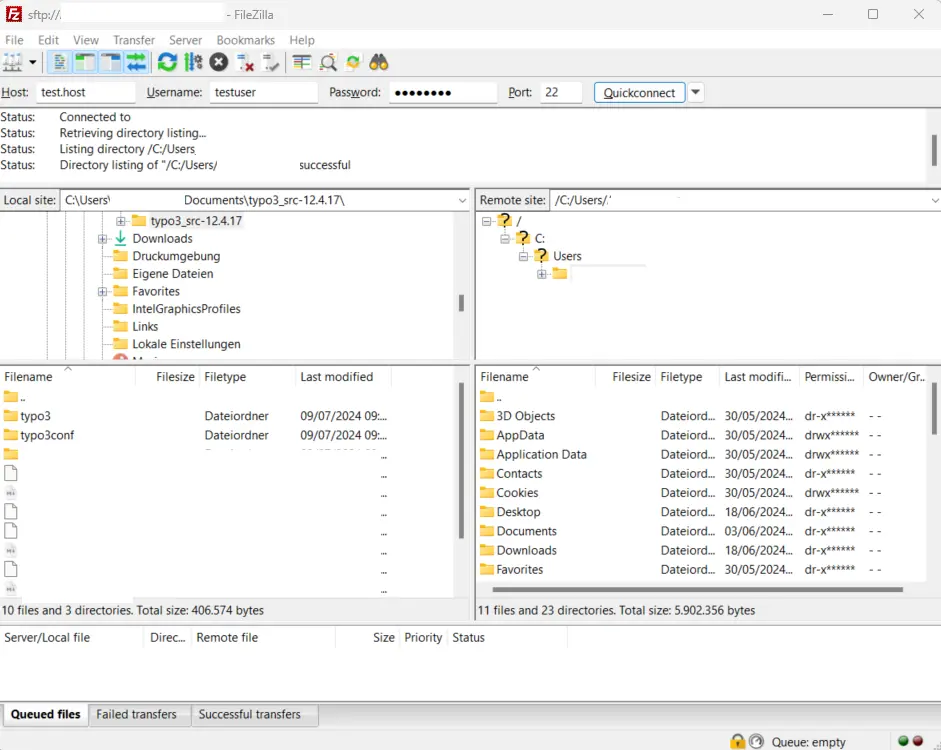
Step 6: Open the FTP program, in this case, FileZilla. To quickly establish a connection to your server, enter your server name under “Host.” Provide your username and password. The system usually auto-completes the port. Then click Quickconnect. The program will attempt to connect to your server. At the bottom of the application, you’ll see your local files in the left-hand pane, while the server directory will appear on the right after a successful connection.
Alternative: Select the “Files” option from the main menu and click on “Site Manager” in the drop-down menu that appears. A new window will pop up. In the Site Manager, enter your server name again under “Host,” as well as your username and password. In this tool, adjust the upload settings for TYPO3 and connect to the server. In the “Transfer Settings” tab, select the transfer mode. Click on “Default” and set a maximum number of simultaneous connections – in this case, six. If you have a firewall protecting your server, select “Passive” and then click “Connect.”
If you only need to upload a few files, simply drag the desired documents from your local files into the server directory. The FTP software will upload the files.
Step 7: In the main menu, select Edit > Settings > Connection. Set a timeout duration of 600 seconds to avoid interruptions. Set the maximum retries to 2. In the left directory pane, select Transfers > File Types and set the default transfer type to Binary.
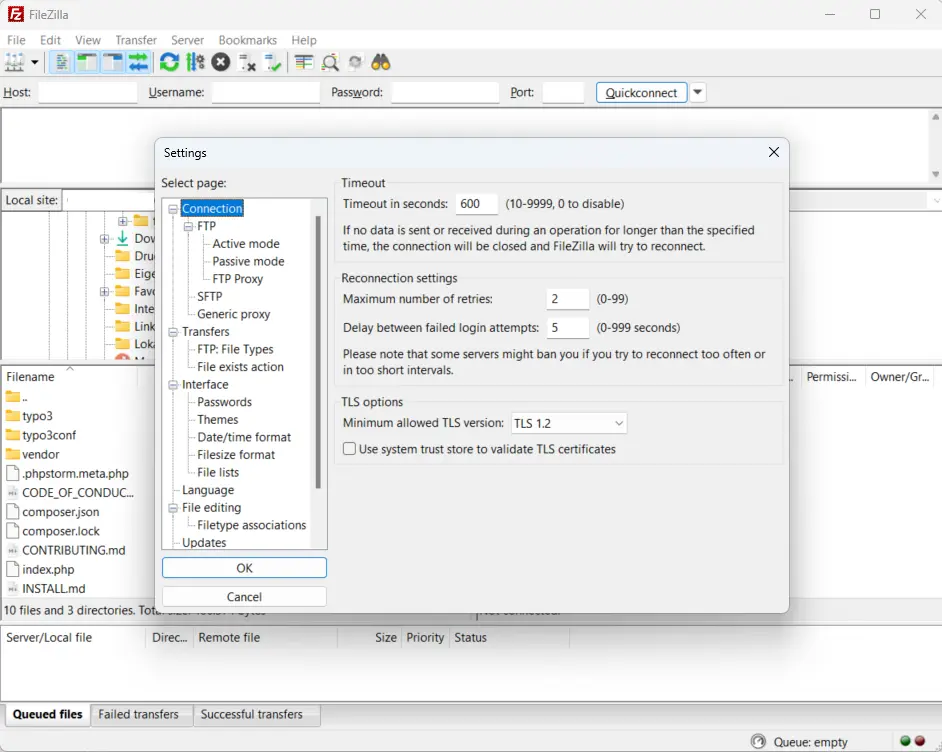
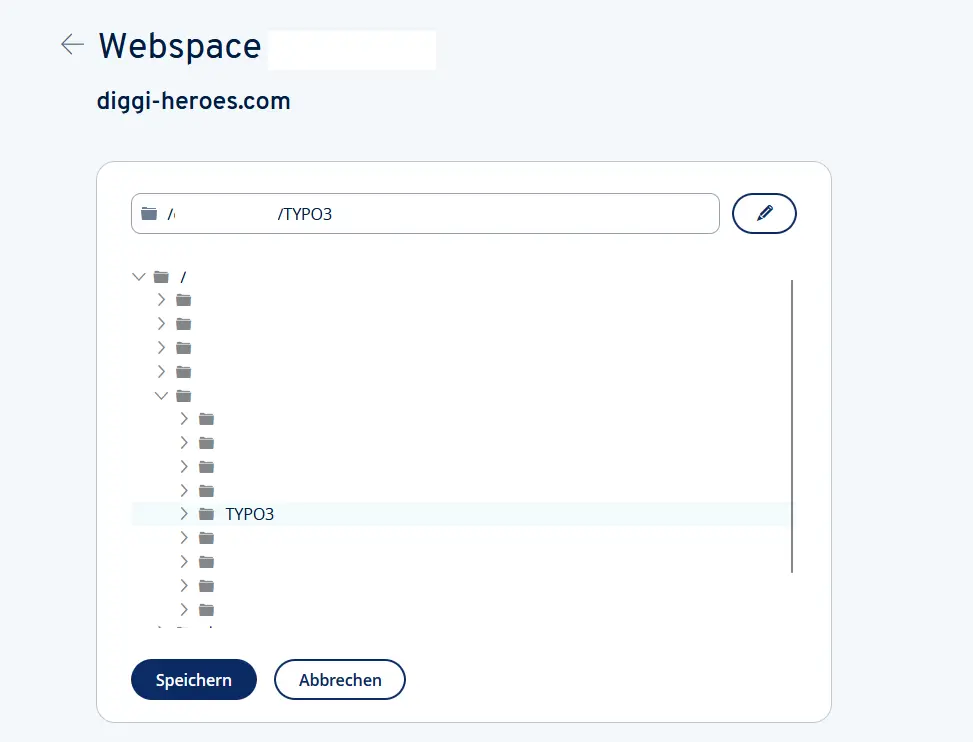
Step 8: Once settings are configured, drag the TYPO3 folder from your local storage (visible in the left-hand pane) to the remote server window on the right. Place the folder in your root directory (denoted as “/” on Unix-like systems).
Step 9: Check if you can find the uploaded files on your server. Log in to your hosting provider to verify. If the files were transferred correctly, you will find them in the hosting section of your webspace. Alternatively, access your TYPO3 installation via the URL localhost/site/.
Step 10: To make your TYPO3-based website publicly accessible, you’ll need a domain. Many hosting plans include at least one domain. If you haven’t chosen a domain yet, register one through your hosting provider.
- Free Wildcard SSL for safer data transfers
- Free private registration for more privacy
- Free Domain Connect for easy DNS setup
Step 11: If you already have a domain, link it to your server. Ensure the path correctly points to your TYPO3 directory.
Step 12: Since the server and domain are now connected, you can proceed with the TYPO3 installation in your browser. Visit the homepage of your new site. A thank-you message from TYPO3 will appear. From here, use the TYPO3 installation tool. To begin, create an empty file named “FIRST_INSTALL” (without an extension) in the root directory of your webspace. Reload your website in the browser.
If the tool does not start, try this alternative. Create a file named “ENABLE_INSTALL_TOOL” (again without a file extension) in the TYPO3 subdirectory typo3config.
Step 13: The installation wizard is accessible at the address https://www.[DOMAIN-NAME].com/typo3/install.php. This tool will guide you through the TYPO3 installation process, which consists of five phases. In the first phase, it checks your system environment. If any issues arise due to a configuration setting, you can use the troubleshooting feature. Otherwise, you can proceed to the next step.
Step 14: In the next step, specify the database TYPO3 will use. If you haven’t set up a database yet, visit your hosting provider’s page. Creating a database is usually done in just a few steps. TYPO3 requires the following database details:
- Database name
- Username for the database
- Password
- Host (often “localhost”)
- Port (commonly 3306)
Step 15: You can now either select an existing database or create a new one. The latter is only possible if you have the necessary permissions.
Step 16: In the next input screen, set a username and password for logging into both the backend and the installation tool. Under “Site name”, enter the name of your new TYPO3 website.
Step 17: In the final step, the assistant completes the installation by automatically adjusting some configurations to your system environment. You can decide whether TYPO3 should create an empty website or remain idle for now. By clicking “Open the TYPO3 Backend”, you will be directed to the admin area, where you can log in using the account you just created. Congratulations, you have successfully installed TYPO3!
For experienced TYPO3 developers, it might be worth configuring everything manually. However, there’s an easier way: IONOS web hosting not only places the installation file on the web server but also supports the subsequent CMS setup with templates and a trained support team.
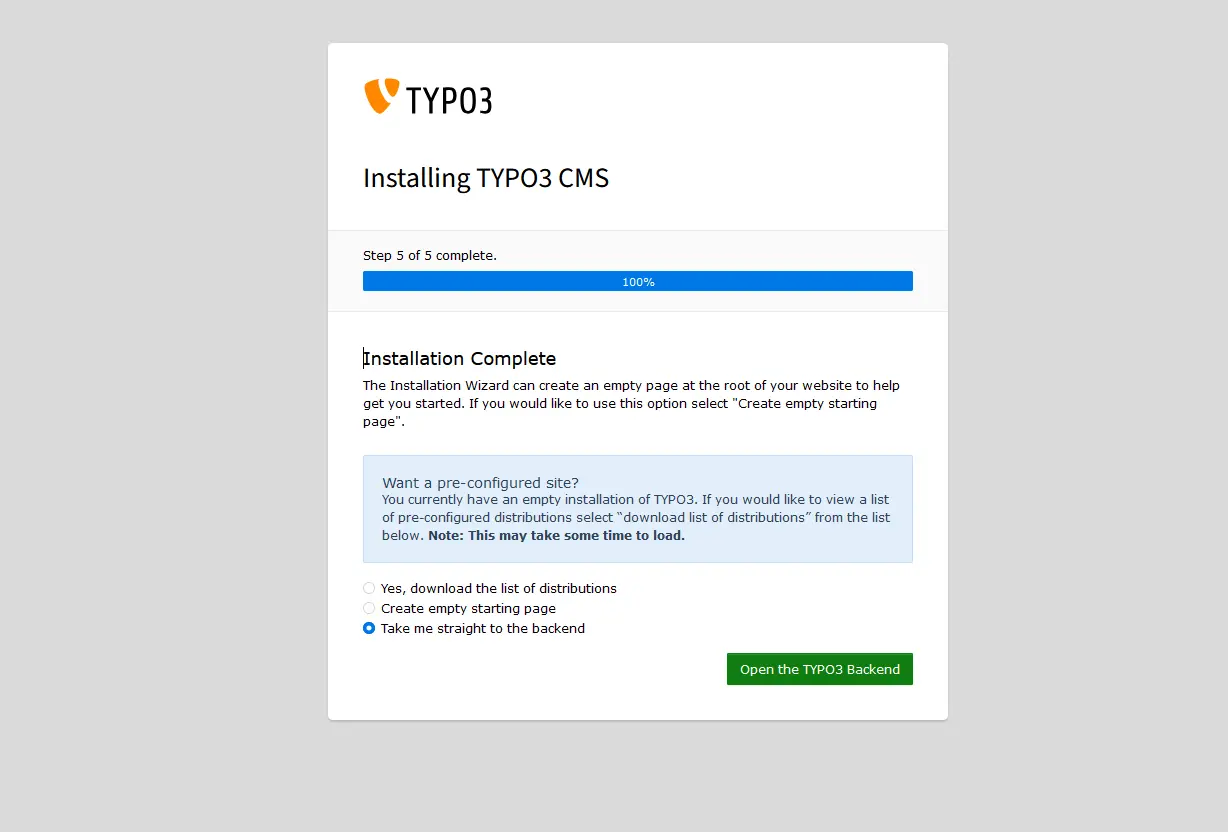
The TYPO3 team recommends locking the installation assistant once you’re done to prevent unauthorized access. However, you can first review basic data or synchronize your database. Through the left column, you can access configurations, perform upgrades, and examine the system environment in case of errors. The Folder Structure allows you to view your directory tree. With Test Setup, you can check whether your settings produce errors. If so, the troubleshooting feature Clean Up can assist you.
From here, proceed to the backend, where you log in with the administrator credentials you previously set up. In the backend, you can customize TYPO3 to your needs, add extensions, or create accounts for editors who will later access the website frontend. The active community provides free templates that you can use for your website. These templates include commands in TYPO3’s internal configuration language, TypoScript. After completing the installation with this guide, you can leverage extensions and templates to customize your website and optimize your backend.
If you want to learn more about the capabilities of the TYPO3 CMS, read our article “TYPO3 – A CMS with Great Functional Diversity”. It also explains how to use TYPO3 templates and customize both the backend and frontend with extensions.

