How to install WordPress Multisite step by step
With WordPress Multisite, you can create and manage multiple websites within a single WordPress installation. This allows you to build a network of separate WordPress sites that you can centrally manage and maintain with Super Administrator privileges. In this guide, you’ll learn how to benefit from WordPress Multisite and how to set up your wp multisite step by step.
- Stress-free, no matter your skill level with easy AI tools
- Fully customizable with themes and plugins
- Hassle-free updating and less admin
Why use WordPress Multisite and what are the benefits?
WordPress Multisite is ideal whenever you need to centrally manage multiple WordPress sites. A WordPress multisite network can serve as the foundation for a wide range of websites. Often, sites within such a network share design and functionality elements. As the “Super Administrator” of a WordPress multisite, you determine which themes (design templates) and plugins are installed globally—making them available to all sites. You also control user roles and permissions, such as assigning sub-admin access (referred to in WordPress as “Users”).
Key advantages of a WordPress multisite setup include, in addition to centralized control, notable savings in time and costs:
- All websites in the network reside within a single WordPress installation, sharing the same themes and plugins—saving disk space.
- All themes and plugins are centrally managed. Updates only need to be applied once, not individually for each site.
- The Super Administrator has comprehensive control, especially regarding design (themes) and functionality (plugins).
Common use cases for WordPress Multisite include:
- Small businesses or individuals who want to create and manage multiple websites efficiently and affordably—e.g. landing pages, regional versions, or brand extensions.
- Enterprises and corporations managing several websites, where centralized control and consistent design help enforce corporate identity.
- Agencies that design, host, and maintain WordPress websites for clients. WordPress multisite provides a relatively simple, cost-effective way to offer services to multiple clients.
Prerequisites before you install WordPress Multisite
You can enable WordPress multisite on an existing installation. Before you begin the WordPress multisite setup, take the following preparatory steps:
- Deactivate all plugins.
- Create a backup of your WordPress site to restore it in case of issues.
- Ensure you have FTP access to edit your WordPress site’s code—either via your hosting provider or a tool like FileZilla.
- Confirm that permalink settings are working properly in your WordPress installation.
- Decide in advance on your preferred URL structure. During the install WordPress multisite process, you must choose between a “subdomain structure” or a “subdirectory structure.” You cannot change this later.
The next sections cover permalink testing and URL structure in more detail.
IONOS offers comprehensive Hosting for WordPress, which allows you to easily create multisite networks.
Test permalink functionality
You’ll find permalink settings in your WordPress dashboard under “Settings.” These determine how your page URLs look, such as https://example.com/?p=123 or https://example.com/page-name. It’s important to ensure that the permalink changes work correctly in your system. If you’re unsure, you should test the permalink settings. When you modify something under the “Common Settings” for permalinks, the browser should display a different URL. To see the changes reflected in your browser, you’ll most likely need to refresh the page.
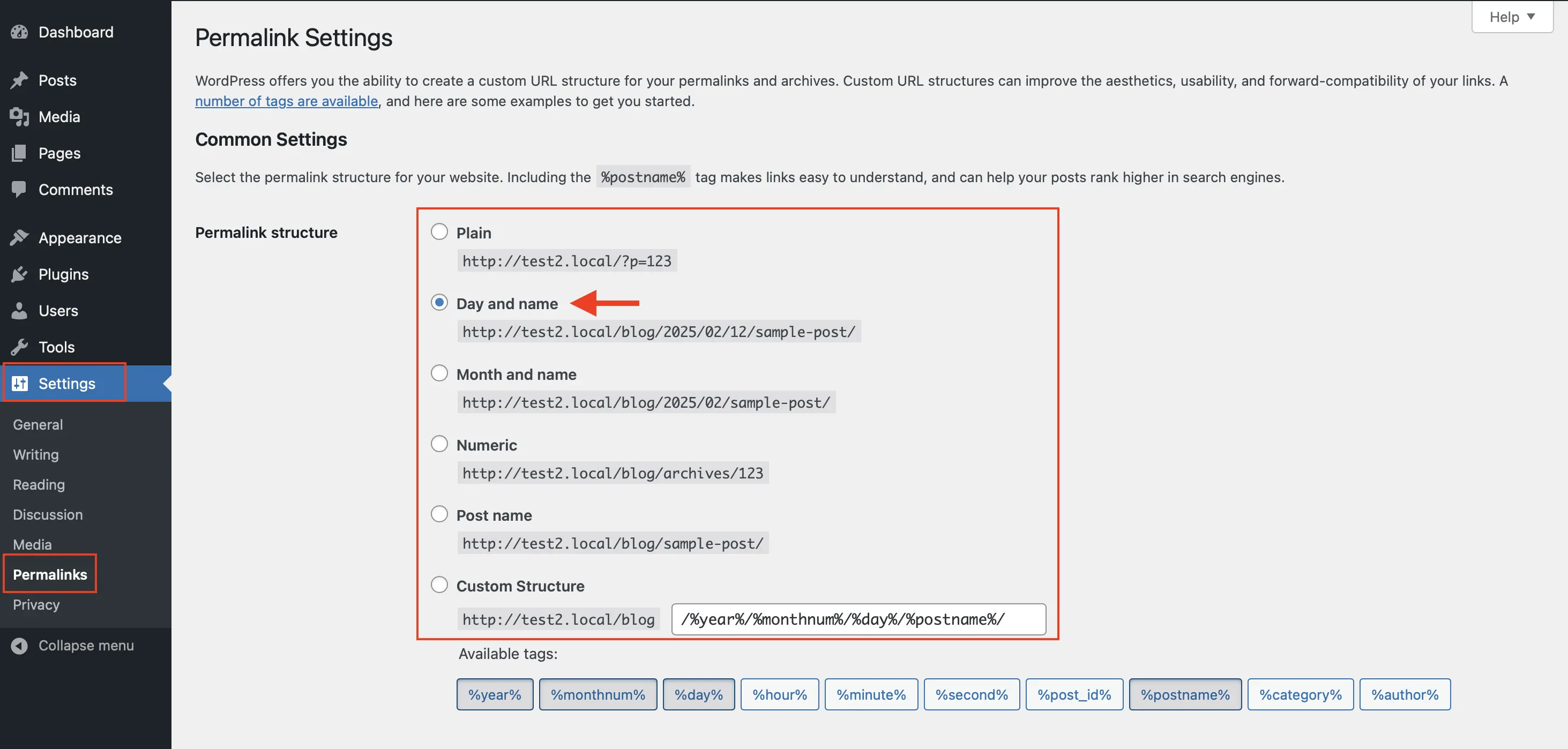
Choose a URL structure for your WordPress Multisite
Before you install your WordPress multisite, you should decide which URL structure you want to use. You can choose between a subdomain structure and a traditional subdirectory structure, which determines how the different sites in your multisite network will be accessed. During the wp multisite setup, you must choose one of these two structures—this decision cannot be changed later.
Subdomain structure example: https://site1.yourdomain.com; https://site2.yourdomain.com; https://site3.yourdomain.com
Subdirectory structure example: https://yourdomain.com/site1; https://yourdomain.com/site2; https://yourdomain.com/site3
The URL structure is an important factor when it comes to search engine optimization (SEO). If you choose a subdomain structure, each subdomain—such as https://site1.your-maindomain.com—is treated by search engines as a separate website. If you opt for a subdirectory structure, all websites within your WordPress multisite network are considered part of a single (larger) website. With a subdomain structure, you’re essentially managing multiple (usually smaller) websites that are indexed independently. With a subdirectory structure, search engines see your wp multisite network as one large site. Both options have their advantages and disadvantages for SEO, so you should carefully consider them in advance. Additionally, keep in mind that search engines like Google update their rules from time to time.
How to set up WordPress Multisite step by step
Once you’ve completed the steps above, you can install WordPress multisite by following this procedure:
- Add a code snippet to the wp-config.php file to enable multisite
- Use the WordPress dashboard to configure the network and generate code snippets
- Insert those code snippets into the wp-config.php and .htaccess files
Add a line of code to wp-config.php
Step 1: Download the WordPress file wp-config.php to your computer and save it locally. You can use your hosting provider’s FTP tool or an FTP client like FileZilla. Some providers also allow you to open, edit, and update the wp-config.php file directly within their system, in which case downloading the file isn’t necessary. Whichever method you choose, make sure that no data is lost during the process.
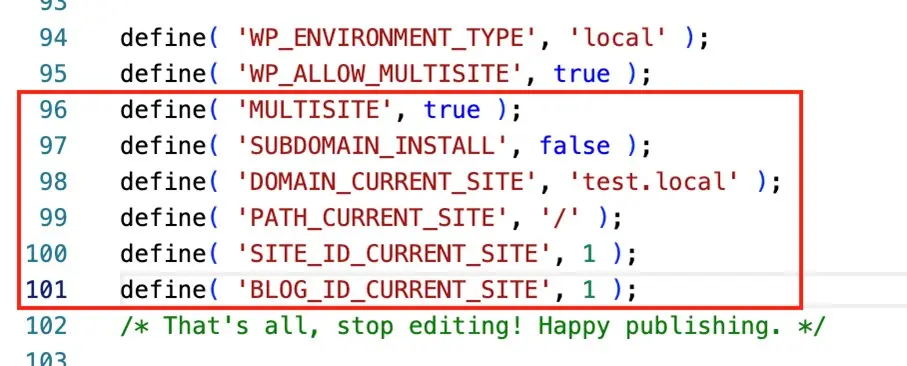
Step 2: Open wp-config.php and find the line:
/ *That’s all, stop editing! Happy publishing.* /Directly above this line, insert the following code snippet:
define( 'WP_ALLOW_MULTISITE', true );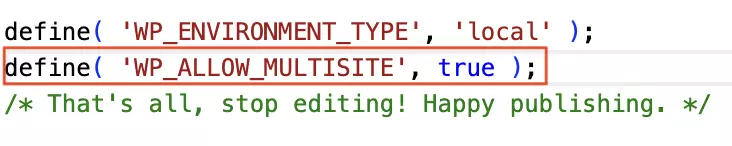
Step 3: Depending on how you completed Step 1, upload the modified wp-config.php file back to your system. If your hosting provider allows it, you can also save and update the file directly within their platform.
Adjust settings in the WordPress dashboard
Step 4: After completing the previous steps, open your WordPress dashboard—you may need to refresh it. In the “Tools” section, you’ll now see a new option called “Network Setup.” When you open it, you can choose whether your new multisite network will use subdomains or subdirectories. Then, enter a network title and your email address as the network administrator. Click “Install” to continue.
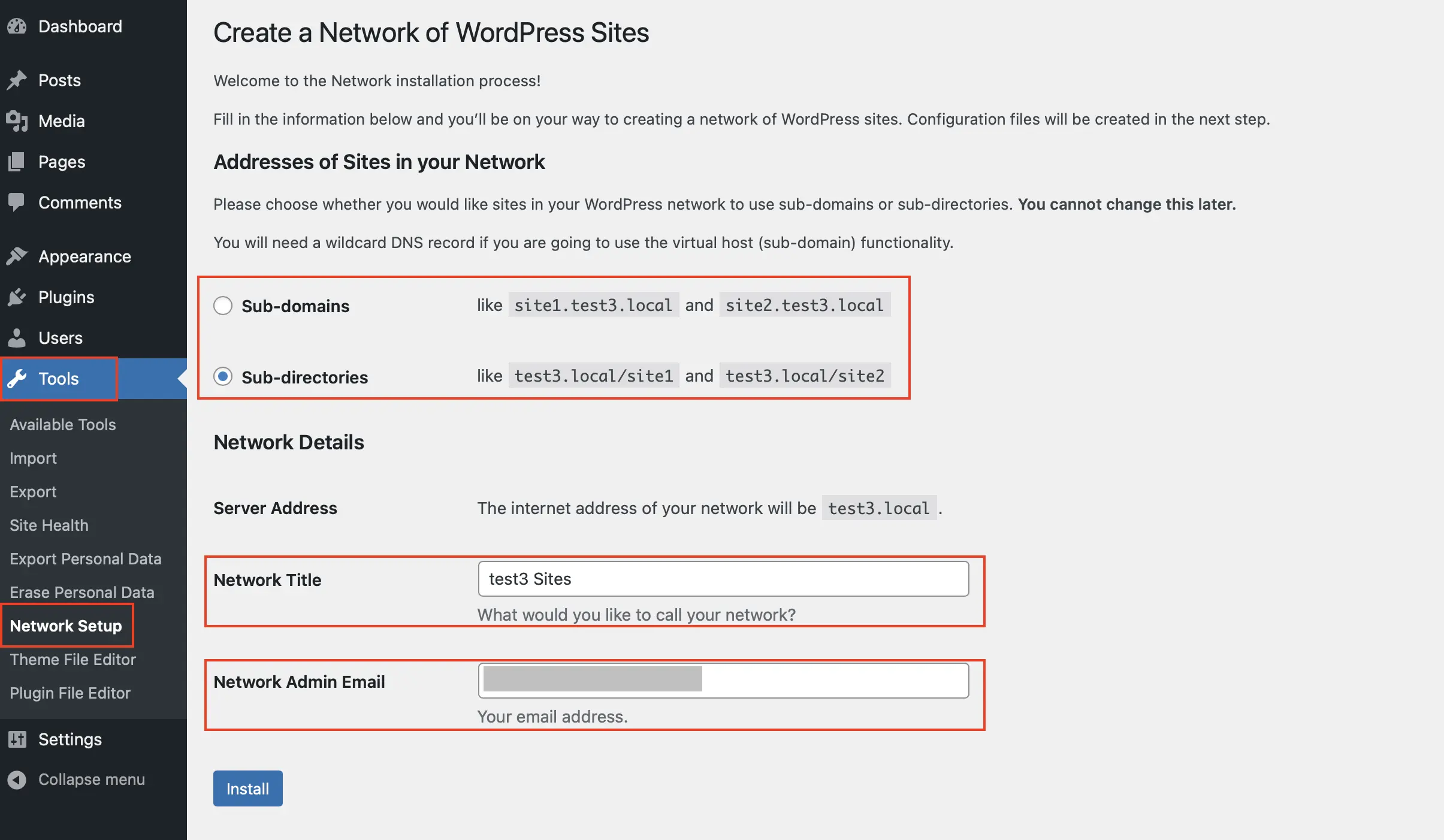
Step 5: After clicking “Install,” WordPress will generate two code snippets on the next screen. You’ll need to copy and paste them into your wp-config.php and .htaccess files as outlined in the next steps.
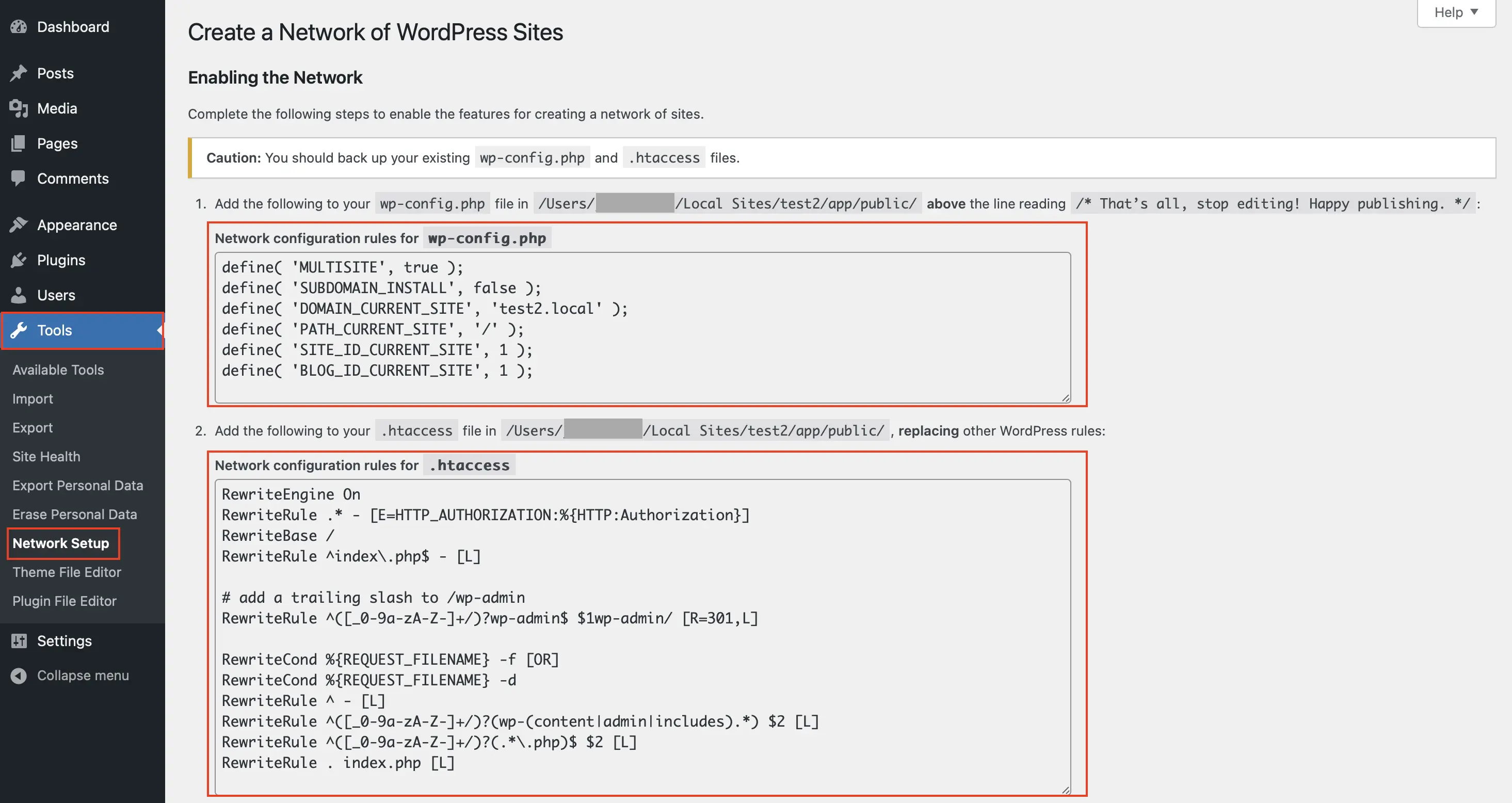
Insert code snippets into wp-config.php and .htaccess
Step 6: Now open the wp-config.php file again, just as you did earlier. Then copy the first code snippet you received from the WordPress dashboard and paste it into the wp-config.php file. Be sure to insert it once again above the following line:
/ *That’s all, stop editing! Happy publishing.* /Then upload the wp-config.php file again, or save and update it directly through your hosting provider.
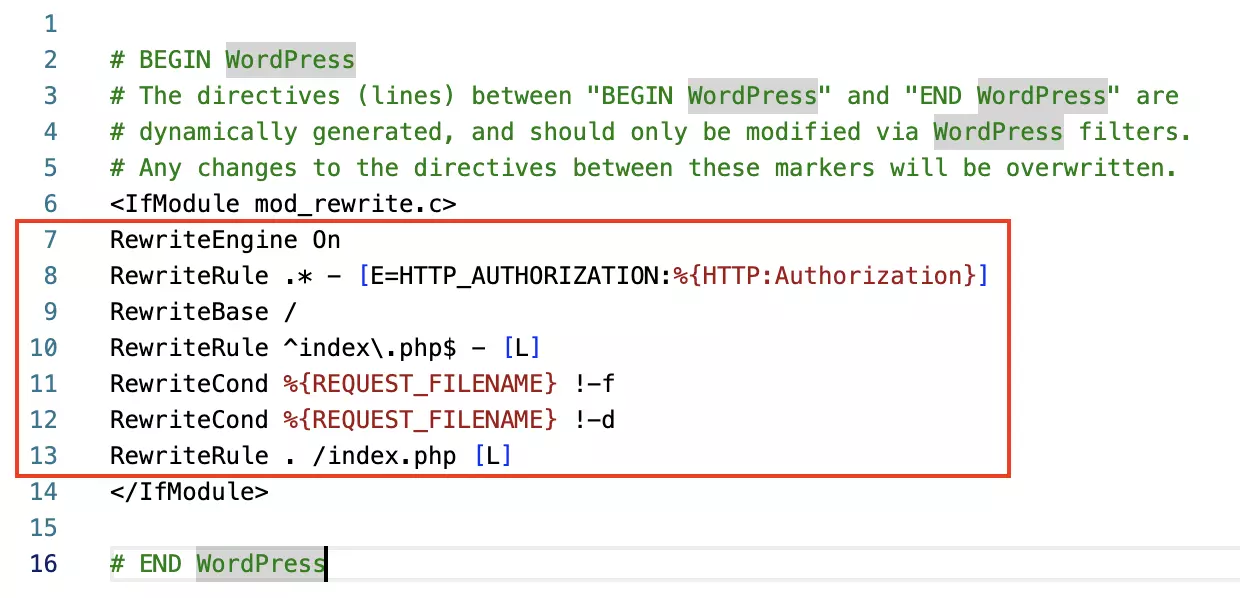
Step 7: Now repeat the process with the second code snippet from the WordPress dashboard and the .htaccess file. In most cases, this means replacing existing code with the code provided by WordPress. A typical .htaccess file with the code to be replaced might look like this:
The updated .htaccess file with the new code would then look like this:
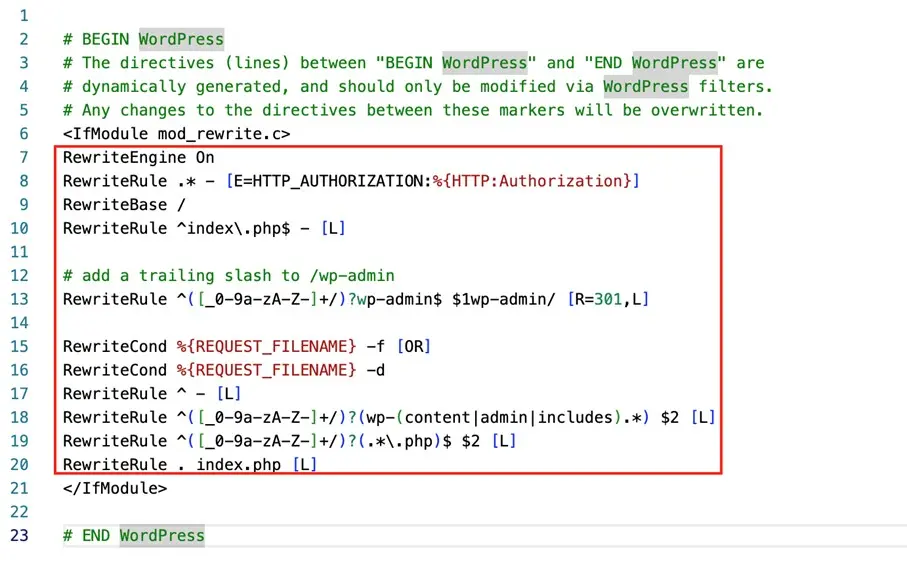
Once the updated .htaccess file is saved or uploaded, your WordPress multisite installation is complete. You can now configure various settings within your WordPress multisite network. To proceed, you’ll need to log back in to WordPress.
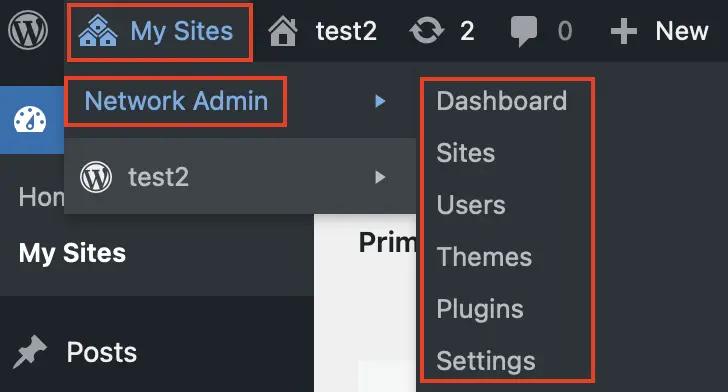
How to configure your network in WordPress multisite
As a Super Administrator with full privileges, you can now configure a variety of settings in your WordPress multisite network. For example, you can add new websites, install new themes and plugins, and also add users with limited admin rights for specific sites in your network.
For general information about WordPress, check out “Create a WordPress website”. For essential security tips, see “WordPress plugins to secure your website”. And for design inspiration, take a look at “Most popular WordPress themes”.


