How to fetch data with PHP mysqli_query?
With PHP, information can be easily retrieved from a MySQL or MariaDB database. A connection to the database is established, and then a SQL query is executed with PHP mysqli_query(), allowing the results to be further processed.
- Enterprise-grade architecture managed by experts
- Flexible solutions tailored to your requirements
- Leading security in ISO-certified data centers
Requirements
To access data from a MySQL or MariaDB database with PHP, a few basic requirements must be met. First, a working PHP environment on the server is necessary, typically in combination with a web server such as Apache or Nginx. If this is not yet available, you will need to install PHP. In addition, MySQL or MariaDB must be installed. On the PHP side, the MySQLi extension is required, though it is already included in most standard installations.
How to retrieve information from MySQL/MariaDB with PHP
In this tutorial, you’ll learn how to set up a basic MySQL/MariaDB database with a table and user, and then connect to it using PHP. Step by step, we’ll build a simple sample website that pulls restaurant reviews from the database and displays them in an HTML table.
Step 1: Create a database
The first step is to create the database. To do this, log in to the MySQL/MariaDB client from the command line:
mysql -u root -pCreate a database for the reviews:
CREATE DATABASE reviews;Switch to this database:
USE reviews;For this example, we will create a single table with four fields:
- ID: The primary key of the table, set to auto-increment.
- Reviewer name: A text field with a maximum length of 100 characters.
- Star rating: A numeric field (TINYINT) for values from 1 to 5.
- Review text: A text field for up to around 500 words (VARCHAR(4000)).
Create the table using the CREATE-TABLE command:
CREATE TABLE user_review (
id MEDIUMINT NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT PRIMARY KEY,
reviewer_name VARCHAR(100),
star_rating TINYINT,
details VARCHAR(4000)
);Now let’s add two sample reviews to the table:
INSERT INTO user_review (reviewer_name, star_rating, details) VALUES ('Ben', '5', 'Love the calzone!');
INSERT INTO user_review (reviewer_name, star_rating, details) VALUES ('Leslie', '1', 'Calzones are the worst.');Step 2: Create a database user
In the next step, create a user for the database. For security reasons, it is recommended to set up a unique user for each database, especially if the database will be accessed from a website.
The following command creates a user named review_site with the password JxSLRkdutW and grants access to the newly created database:
CREATE USER 'review_site'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'JxSLRkdutW';
GRANT SELECT ON reviews.* TO 'review_site'@'localhost';Step 3: Create a PHP script
The code in this tutorial is simplified to illustrate examples. When creating a real website, it is strongly recommended to follow common security best practices to ensure that your PHP scripts do not compromise server access.
Create a file named showreviews.php in your webspace and open it for editing. For example, to create the file in the /var/www/html directory using the nano editor, run the following command:
sudo nano /var/www/html/showreviews.phpIn this example, PHP is embedded within HTML, so the page starts with the basic HTML declarations. The CSS styling is also included in the HTML head:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta-charset="utf-8">
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
margin: 20px auto;
width: 80%;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px 10px;
text-align: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>Every PHP script must begin with the PHP opening tag:
<?phpNext, add a MySQL/MariaDB connection block that includes the server location (localhost), the database name, and the database username and password.
$hostname = "localhost";
$username = "review_site";
$password = "JxSLRkdutW";
$db = "reviews";Next, add a section to establish a connection to the database. If the connection fails, an error message will appear. In both MySQL and MariaDB, you can connect your PHP script to the database using mysqli_connect(). This function requires the hostname, username, password, and database name, so PHP knows exactly which database to access.
$dbconnect=mysqli_connect($hostname,$username,$password,$db);
if (!$dbconnect) {
die("Database connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
?>Step 4: Insert the table
In the next step, add the HTML code to your script to create the table structure that will be used to display the data:
<table>
<tr>
<td>Reviewer Name</td>
<td>Stars</td>
<td>Details</td>
</tr>Next, add the PHP code that queries the database and loops through the results, displaying each review in its own table row:
<?php
$query = mysqli_query($dbconnect, "SELECT * FROM user_review")
or die (mysqli_error($dbconnect));
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_array($query)) {
echo
"<tr>
<td>{$row['reviewer_name']}</td>
<td>{$row['star_rating']}</td>
<td>{$row['details']}</td>
</tr>\n
}
?>Finally, remember to close the table and the HTML block at the end of the document:
</table>
</body>
</html>To test the script, open showreviews.php in your web browser.
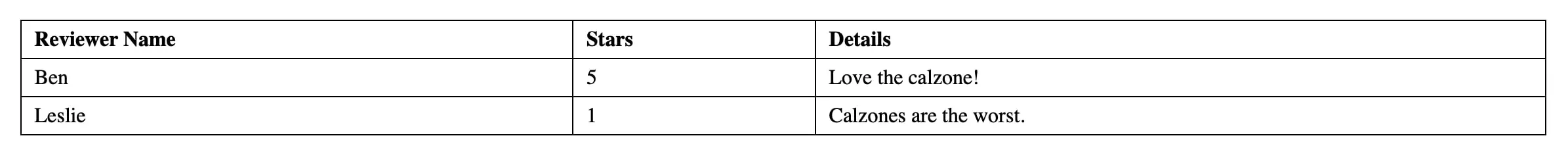
Step 5: Overview of the completed script
The complete PHP script is as follows:
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta-charset="utf-8”>
<style>
table {
border-collapse: collapse;
margin: 20px auto;
width: 80%;
}
th, td {
border: 1px solid black;
padding: 5px 10px;
text-align: left;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<?php
$hostname = "localhost";
$username = "review_site";
$password = "JxSLRkdutW";
$db = "reviews";
$dbconnect=mysqli_connect($hostname,$username,$password,$db);
if (!$dbconnect) {
die("Database connection failed: " . mysqli_connect_error());
}
?>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Reviewer Name</td>
<td>Stars</td>
<td>Details</td>
</tr>
<?php
$query = mysqli_query($dbconnect, "SELECT * FROM user_review")
or die (mysqli_error($dbconnect));
while ($row = mysqli_fetch_array($query)) {
echo
"<tr>
<td>{$row['reviewer_name']}</td>
<td>{$row['star_rating']}</td>
<td>{$row['details']}</td>
</tr>\n";
}
?>
</table>
</body>
</html>
