How to create an online store with WordPress WooCommerce step by step
Today, having your own online store is essential for growing brand visibility and driving sales. If you like working with the WordPress CMS, the WooCommerce plugin provides a convenient way to launch and manage a full-featured e-commerce project.
- Stress-free, no matter your skill level with easy AI tools
- Fully customizable with themes and plugins
- Hassle-free updating and less admin
Why create an online store?
As a provider of high-quality products, you not only want to offer your customers easy access to your range but also convince them of your offering’s quality. By designing a mobile-friendly store, you respond to changing purchasing behaviors (shopping increasingly happens on the go or via smartphone) and reach even more potential customers. Whether you sell physical products or offer digital content for download, a professional web shop allows you to manage your inventory, coordinate customer orders and shipping, implement marketing strategies, and enhance discoverability in search engines with targeted SEO measures. This makes it faster and easier for users to find your store online.
If you’re familiar with content management systems, you have the opportunity to create your own online store with the popular solution WordPress. The advantage of WordPress is that it’s a globally recognized open-source system offering numerous features. Through WordPress’s user-friendly dashboard, a store can be easily set up, managed, and expanded with various extensions, known as WordPress shop plugins.
One of the most common ways to use WordPress for e-commerce is by integrating WooCommerce, a powerful, free shop extension. The free version already offers many features for a professional store, which can be enhanced with paid premium features if needed. For beginners, WooCommerce provides a solid foundation for a functional store even without additional premium features.
At IONOS, you can easily use WordPress with an online store through Hosting for WooCommerce.
Step 1: Install WordPress store with WooCommerce
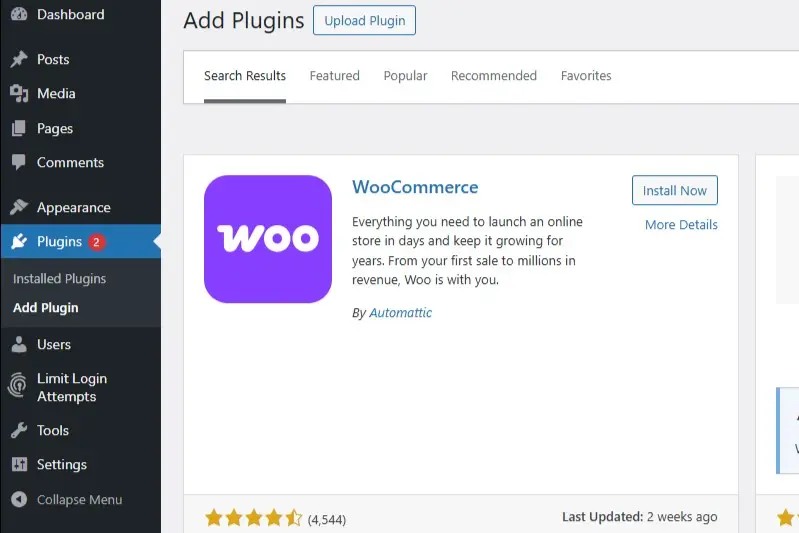
To use WooCommerce, you first need to install the plugin in WordPress. In the dashboard, go to “Plugins” and click on “Add Plugin.” Enter “WooCommerce” in the search field. Once the plugin appears, click on “Install Now” and then “Activate.” For newcomers, it’s recommended to use the integrated setup wizard, which guides you step-by-step through the installation.
The basic settings can be adjusted at any time later and include, among other things:
- Business location
- Currency
- Unit of measurement for product weights
- Tax and shipping options
- Payment options
Step 2: Set up the online store in the general settings
Under “Settings” and “General,” you can set basic information such as the website title, web address (URL), timezone, and site language. More important settings are available under the “WooCommerce” -> “Settings” menu, where you can manage various aspects of the shop:
- Products: Here you can set product-specific options such as units of measurement, reviews, inventory management, and digital products.
- Payments: In this menu, you manage payment options, such as PayPal, bank transfer, cash on delivery, and many others. You will also find tax options here, where you can set sales tax and other tax rates for your products.
- Shipping: Define shipping options for different countries and regions.
- Accounts and privacy: Decide how and where users are directed for registering or logging into their customer accounts. You can also set whether and how customer accounts can be created. Additionally, there are options for privacy policy management.
- Emails: Under “Emails,” you can configure individual email notifications for customer transactions. You can freely choose the type of notification (e.g., for new, canceled, or failed orders) and the recipients.
Step 3: Design and navigate your online store
User-friendliness is crucial for your store’s success. WooCommerce automatically creates a main navigation with the basic menu items “Shop,” “Cart,” “Checkout,” and “My Account.” You can further customize and expand these in the “Design” section of the Site Editor. Depending on the theme, you can also design the layout and color scheme of your store. The type of design and color impact that best suits your store depends, among other things, on your industry, the product range, and of course, the preferences of your target audience.
Step 4: Add products, texts, and images to the WordPress online store
To add products, select the option “Add New Product” under “Products” in the left sidebar menu. In the product edit screen, you can enter the product name, description, images and media, and other essential details like price, inventory management, and shipping options. You can also set up product variations if the product is available in different options (e.g., colors, sizes). The product pages provide your customers with detailed information about each item and are the focal point for sales. Ensure the pages are attractively designed and include all relevant information to encourage purchases.
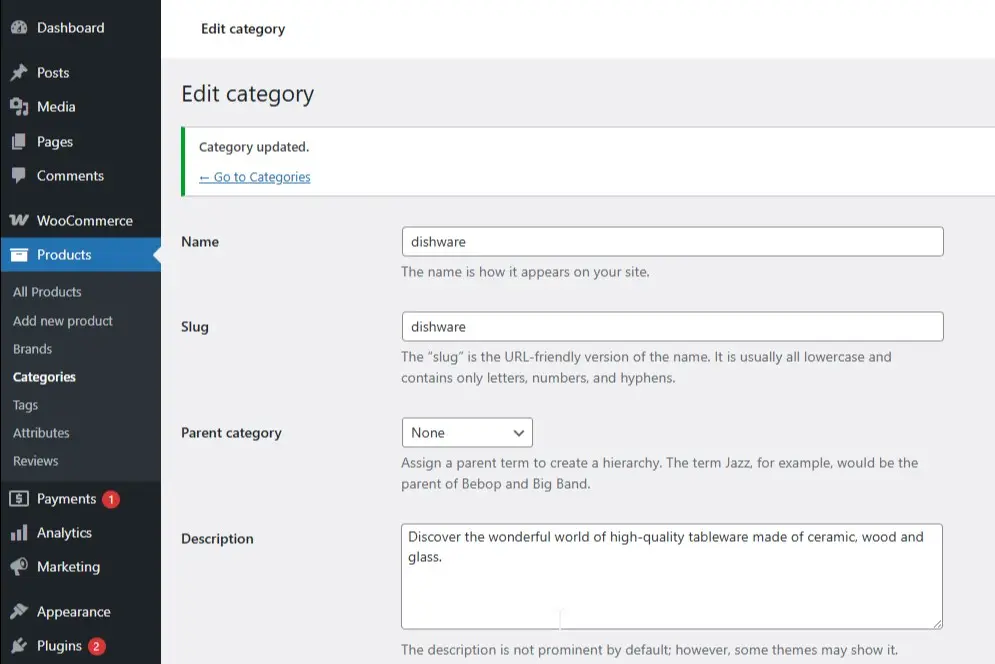
Furthermore, you can organize products into categories to better structure your store. To do this, go to “Categories” in the “Products” menu and create new categories for your products. This makes it easier for your customers to navigate and find the desired items. Category pages are particularly important for user navigation as they offer an overview of similar products and help customers quickly find the right product. Ensure each category contains a clear and precise description to help both users and search engines understand the content correctly.
To provide complete product information, you should include precise details such as clear URLs, titles, and short descriptions. A well-organized structure and relevant metadata enhance both user experience and search engine optimization (SEO), increasing the reach of your store.
Step 5: Additional features for your WordPress online store
WooCommerce offers many additional features that you can activate as needed, such as coupons, order management, and reporting.
Orders
Once you have paying customers, you can manage and edit all customer orders under the “Orders” section. Here, you can view the status, contact details, order date, billing and shipping information, as well as the product overview.
Coupons
Coupons offer an incentive to buy. Through the coupon menu, you can set discounts for carts or products, determine amounts and validity periods, and define order value limits.
Reports
In the “Reports” menu, you can view the development of orders and revenue. Key metrics such as sales, orders, and shipping costs are displayed. A flexible timeline allows you to filter the data as desired.
How to create an online store with WordPress for an easy start in e-commerce
By creating your online store with WordPress, you ensure easy management of your offerings online. While using a free CMS like WordPress (as opposed to integrated webshop software like Shopware or Magento) may require some compromise on performance, scope, and functionality, it can be worthwhile for beginners with a manageable inventory to easily design their own online store with WordPress.
The WooCommerce plugin is a valuable addition thanks to its user-friendliness and numerous customization options. Once you have set up and stocked your store, you should conduct a test run as a “customer” to ensure all shop elements (search, order, cart, etc.) function smoothly. After that, you can proceed with launching and further developing your WordPress store.
Advantages and disadvantages of creating a WordPress online store with WooCommerce
| Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|
| ✓ Free installation and quick setup via CMS | ✘ Limited performance for stores with a large inventory |
| ✓ Central management and full control over all key e-commerce processes | ✘ Requires additional plugins for certain legal or compliance features, depending on the market |
| ✓ Simple and flexible operation | ✘ No integrated inventory management functions |
| ✓ Integration of numerous interfaces (themes) and extensions | ✘ Solid training in content management with WordPress is necessary |
| ✓ Especially practical for smaller inventories and digital product offerings | ✘ Some plugins require a fee |


