What is a crawler? How data spiders optimize the internet
Web crawlers are the reason search engines like Google, Bing, Yahoo, and DuckDuckGo can always deliver current and new search results. Like spiders, bots roam the web, collect information, and store it in indexes. But where else are web crawlers used, and what different types of crawlers exist on the World Wide Web?
- Improve your Google ranking without paying an agency
- Reply to reviews and generate social media posts faster
- No SEO or online marketing skills needed
What is a crawler?
Web crawlers are bots that search the internet for data. They analyze content and store information in databases and indexes to improve the performance of search engines. Additionally, they collect contact and profile data for marketing purposes.
Since crawler bots navigate the web and its countless branches in search of information with the same ease as spiders, they’re often referred to as spider bots. Other common names include search bots and web crawlers. The very first crawler, called the World Wide Web Wanderer (or simply WWW Wanderer), was developed using the PERL programming language. Launched in 1993, the WWW Wanderer tracked the growth of the then-nascent internet and stored its findings in the first internet index known as Wandex.
Web crawlers are especially important for search engine optimization (SEO). It’s essential for businesses to become familiar with the different types and functions of web crawlers to provide SEO-optimized content online.
How does a crawler work?
Just like social bots and chatbots, crawlers are made up of a code of algorithms and scripts that assign specific tasks and commands. The crawler independently and continuously repeats the functions set in the code.
Web crawlers move through the web using hyperlinks from existing websites. They evaluate keywords and hashtags, index the content and URLs of each site, copy webpages, and open all or a selection of found URLs to analyze new websites. Additionally, crawlers check the currency of links and HTML codes.
Through specialized web analysis tools, web crawlers can evaluate information like page views and links, and collect data in the context of data mining, or specifically compare data (e.g., for comparison portals).
Search engines and specialized crawlers are increasingly using artificial intelligence and Natural Language Processing (NLP) to understand web content not only technically but also contextually. Modern crawlers can analyze semantic relationships, topic relevance, or text quality.
What are the different types of crawlers?
There are different web crawlers that vary in their focus and scope.
Search engine crawlers
The oldest and most common type of web crawler are the search bots from Google or alternative search engines like Yahoo, Bing, or DuckDuckGo. They review, collect, and index web content, thereby optimizing reach and the search engine database. The names of the most well-known web crawlers are:
- GoogleBot (Google)
- Bingbot (Bing)
- DuckDuckBot (DuckDuckGo)
- Baiduspider (Baidu)
- Yandex Bot (Yandex)
- Sogou Spider (Sogou)
- Exabot (Exalead)
- GPTBot (OpenAI)
- ClaudeBot (Anthropic)
Personal website crawler
These small web crawlers are simple in function and can be used by individual companies to perform specific tasks. For example, they monitor the frequency of certain search terms or the accessibility of specific URLs.
Commercial website crawlers
Commercial web crawlers are complex software solutions from companies offering web crawlers as purchasable tools. They provide more services and features, saving a company the time and costs required for developing its own crawler.
Cloud website crawlers
There are also website crawlers that store data not on local servers, but in a cloud and are usually commercially distributed as a service by software companies. Due to the independence from local computers, the analysis tools and databases can be accessed from any device with the appropriate login credentials. Additionally, the applicability can be scaled.
Desktop website crawlers
You can also run small web crawlers on your own PC or laptop. These very limited, affordable crawlers can usually only analyze small amounts of data and websites.
Mobile crawlers
Mobile crawlers analyze websites as they are displayed on smartphones and tablets. Since Google’s shift to mobile-first indexing, they are crucial for search engine ranking. They can, for example, identify display issues and evaluate them accordingly.
AI crawlers
AI crawlers are AI-based web crawlers. They are used by companies to analyze, evaluate, or utilize web content for training large language models (LLMs). Unlike classic search engine bots, they don’t just index websites; they understand content on a semantic level, extract knowledge, and use it to enhance models.
- Our experts run your campaign
- Increase your online visibility
- Save money thanks to greater efficiency
How do crawlers work in practice?
The specific procedure of a web crawler consists of several steps:
-
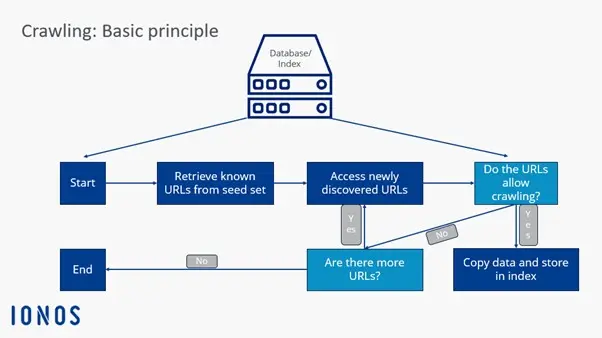
Crawl frontier: Search engines use a data structure called the crawl frontier to determine whether web crawlers should explore new URLs through known, indexed websites and links specified in sitemaps, or only crawl specific websites and content.
-
Seed set: Web crawlers receive a seed set from the search engine or client. The Seed Set is a list of known or to-be-explored web addresses and URLs. This set is based on previous indexings, databases, and sitemaps. Crawlers explore the set until they reach loops or dead links.
-
Index addition: Through seed analysis, web crawlers can evaluate new web content and add it to the index. They update old content or remove URLs and links from the index when they no longer exist.
-
Crawling frequency: While web crawlers are continuously active online, developers can control how often specific URLs are revisited and analyzed. Factors such as page performance, update frequency, and user traffic are evaluated to determine how frequently a page should be crawled.
-
Index management: Website administrators can specifically prevent web crawlers from visiting their site. This is possible through robots.txt protocols or
nofollowHTML tags. When accessing a URL, crawlers receive instructions to avoid or only partially evaluate a website.
Since 2020, Google has no longer treated the nofollow attribute as a strict instruction but rather as a hint when assessing links. This change means that nofollow links may still be crawled and indexed. For website owners looking to prevent content from being crawled, it’s important to also use mechanisms like robots.txt or the noindex tag for more reliable control.
What are the advantages of web crawlers?
✓ Cost-effective and efficient: Web crawlers handle time-consuming and costly analysis tasks, scanning, analyzing, and indexing web content faster, cheaper, and more comprehensively than humans.
✓ Easy to use, wide reach: Web crawlers can be quickly and easily implemented, ensuring comprehensive and continuous data collection and analysis.
✓ Enhance online reputation: Web crawlers can optimize online marketing by expanding and focusing the customer spectrum. Additionally, crawlers can improve a company’s online reputation by capturing communication patterns in social media.
✓ Targeted advertising: Through data mining and targeted advertising, specific customer groups can be addressed. Websites with high web crawler frequency are ranked higher in search engines and receive more views.
✓ Evaluate company and customer data: Companies can use web crawlers to evaluate and analyze online available customer and company data, utilizing it for their marketing and business strategy.
✓ SEO optimization: By evaluating search terms and keywords, focus keywords can be defined to limit competition and increase page views.
Additional use cases include:
- Ongoing system monitoring to identify security vulnerabilities
- Preservation of outdated or legacy websites
- Comparing current websites with previous versions
- Identifying and eliminating broken links
- Analyzing keyword search trends
- Spotting spelling mistakes and other content errors
How can the crawling frequency of a website be increased?
If you want your website to rank as high as possible in search engines and be regularly visited by web crawlers, you should make it as easy as possible for the bots to find your website. Those with a high crawling frequency receive higher priority in search engines. For a website to be easily found by crawlers, the following factors are crucial:
- The website has various outbound links and is also linked on other websites. This way, crawlers can find your website not only through links but can also evaluate the website as a connecting node and not just as a one-way street.
- The website content is always updated and kept current. This applies to content, links, and HTML code.
- The availability of the server is ensured.
- The website’s load time is good.
- There are no duplicate or unnecessary links and content.
- Sitemap, robots.txt, and http response headers already provide important information about the website to the crawler.
What is the difference between web crawlers and scrapers?
Although they are often equated with each other, web crawlers and scrapers do not belong to the same type of bot. While web crawlers primarily search for, index, and evaluate web content, scrapers mainly have the task of extracting data from websites through web scraping.
Although there are overlaps between a crawler and a scraper, and crawlers often apply web scraping by copying and storing web content, their main functions are retrieving URLs, analyzing content, and expanding the index with new links and URLs.
Scrapers, on the other hand, primarily function to visit specific URLs, extract specific data from websites, and store it in databases for future use.

